Phenome-wide association of APOE alleles in the All of Us Research Program
- PMID: 40451134
- PMCID: PMC12162039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105768
Phenome-wide association of APOE alleles in the All of Us Research Program
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein E (APOE) variation is associated with altered lipid metabolism, as well as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disease. Prior studies are largely limited to European ancestry populations and differential risk by sex and ancestry has not been widely evaluated.
Methods: We utilised a phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) to explore APOE-associated phenotypes in the All of Us Research Program. We determined APOE alleles for 181,880 participants, representing seven ancestry groups. We tested association of APOE variants, ordered based on Alzheimer's disease risk hierarchy (ε2/ε2 < ε2/ε3 < ε3/ε3 < ε2/ε4 < ε3/ε4 < ε4/ε4), with 2318 phenotypes. Bonferroni-adjusted analyses were performed overall, by ancestry, by sex, and with adjustment for social determinants of health (SDOH).
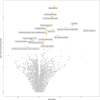
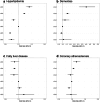
Findings: In the overall cohort, PheWAS identified 17 significant associations, including increased odds of hyperlipidaemia (OR 1.15 [1.14-1.16] per APOE genotype group; P = 1.8 × 10-129), dementia, and Alzheimer's disease (OR 1.55 [1.40-1.70]; P = 5 × 10-19), and reduced odds of fatty liver disease and chronic liver disease. ORs were similar after SDOH adjustment and by sex, except for an increased number of cardiovascular associations in males, and decreased odds of noninflammatory disorders of vulva and perineum in females. Significant heterogeneity was observed for hyperlipidaemia and mild cognitive impairment across ancestry. Unique associations by ancestry included transient retinal arterial occlusion in the European ancestry group, and first-degree atrioventricular block in the American Admixed/Latino ancestry group.
Interpretation: We replicate extensive phenotypic associations with APOE alleles in a large, diverse cohort. We provide a comprehensive catalogue of APOE-associated phenotypes and evidence of unique phenotypic associations by sex and ancestry, as well as heterogeneity in effect size across ancestry.
Funding: Funding is listed in the Acknowledgements section.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Apolipoprotein E; Health disparities; Hypercholesterolaemia; Phenome-wide association study.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.W. is supported by National Institutes of Health awards U01DE034176, U24HG010136, R01HG002939, R21HG012283, and R01GM132600; by National Science Foundation award 1933305; and by Department of Energy Award PerCon SFA. T.W. is an executive advisory committee member for the Montana IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence. E.M.R. is Co-Founder and Advisor for ALZPath.
Figures


Update of
-
Phenome-Wide Association of APOE Alleles in the All of Us Research Program.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 4:2024.09.04.24313010. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.24313010. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: EBioMedicine. 2025 Jul;117:105768. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105768. PMID: 39281754 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Mahley R.W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science (New York, NY) 1988;240(4852):622–630. - PubMed
-
- Farrer L.A., Cupples L.A., Haines J.L., et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA. 1997;278(16):1349–1356. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL156993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026556/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C OD023196/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025315/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026551/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026552/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026549/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025337/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026555/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026550/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026553/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023205/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025276/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026554/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023163/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023206/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG069453/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023176/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026548/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023121/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025277/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL172036/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026557/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD036485/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

