Isorhamnetin ameliorates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in female rats by regulating the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, bone morphogenetic protein 2 and runt-related transcription factor 2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40451839
- PMCID: PMC12246561
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.25-0006
Isorhamnetin ameliorates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in female rats by regulating the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand, osteoprotegerin, bone morphogenetic protein 2 and runt-related transcription factor 2 signaling pathway
Abstract
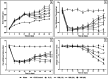
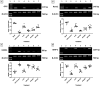
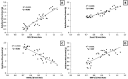
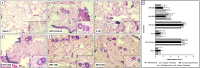
Osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone density and increased fracture risk. The present study assessed anti-osteoporotic effects of isorhamnetin on ovariectomy (OVX)-induced osteoporosis in female rats. Osteoporosis was induced in OVXX-female Sprague-Dawley rats by using Freund's Complete Adjuvant and randomly divided into the following groups (n=15): OVX control, alendronate (3 mg/kg, subcutaneous), and isorhamnetin (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg, p.o.), and received treatment for five weeks after OVX. In results following OVX, significant alterations in behavioral, biochemical, and histological parameters were observed. Conversely, isorhamnetin (20 and 40 mg/kg) treatment significantly improved (P<0.05) OVX-induced alterations in body, femur, and uterine weight, bone mineral content and density, but also effectively mitigated (P<0.05) elevated allodynia and hyperalgesia. It notably improved (P<0.05) changes in serum alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-I), serum and urinary calcium, and phosphorus levels. Isorhamnetin markedly attenuated elevated (P<0.05) serum TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 levels but increased (P<0.05) serum IL-4 and IL-10 levels. Furthermore, mRNA expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG), runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) was upregulated (P<0.05), whereas receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) was downregulated (P<0.05). Histological analysis demonstrated that isorhamnetin effectively improved (P<0.05) OVX-induced inflammation, thereby preventing cellular infiltration, synovial hyperplasia, cartilage erosion, and pannus formation in bone specimens. In conclusion, isorhamnetin exerts its anti-osteoporotic potential by modulating pain (allodynia and hyperalgesia), serum biomarkers (osteocalcin, CTX-I, TNF-α, ILs), and bone signaling pathways (RANKL, OPG, BMP-2, Runx2).
Keywords: isorhamnetin; osteocalcin; osteoporosis; osteoprotegerin; pro-inflammatory cytokines; receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest concerning this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Columbianadin Ameliorate Osteoporosis Against Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis in Rats via Alteration of RANK/RANKL/OPG Signaling Pathway.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Aug;39(8):e70432. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70432. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40791102
-
Plastrum Testudinis Stimulates Bone Formation through Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway Regulated by miR-214.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Aug;31(8):707-716. doi: 10.1007/s11655-025-4012-9. Epub 2025 May 13. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 40358879
-
Anti-osteoporosis effect of Semen Cuscutae in ovariectomized mice through inhibition of bone resorption by osteoclasts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114834. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114834. Epub 2021 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34801609
-
Clinical insights into the role of smoking, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis in osteoporotic fractures.Arch Osteoporos. 2025 Jul 11;20(1):87. doi: 10.1007/s11657-025-01575-8. Arch Osteoporos. 2025. PMID: 40643730 Review.
-
[Retrospective study on intervention of traditional Chinese medicine in osteoporosis and related pain diseases].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Jun;50(11):3180-3188. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250213.702. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40686186 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Anagnostis P, Paschou SA, Mintziori G, Ceausu I, Depypere H, Lambrinoudaki I, Mueck A, Pérez-López FR, Rees M, Senturk LM, Simoncini T, Stevenson JC, Stute P, Trémollieres FA, Goulis DG. 2017. Drug holidays from bisphosphonates and denosumab in postmenopausal osteoporosis: EMAS position statement. Maturitas 101: 23–30. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.04.008 - DOI - PubMed

