Association between cesarean delivery and childhood allergic diseases in a longitudinal population-based birth cohort from Japan
- PMID: 40451859
- PMCID: PMC12127461
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03703-3
Association between cesarean delivery and childhood allergic diseases in a longitudinal population-based birth cohort from Japan
Abstract
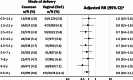
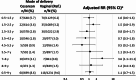
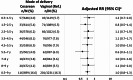
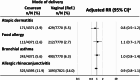
The association between cesarean delivery and childhood allergic diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, food allergy, and bronchial asthma, remains unclear, with limited evidence from Asian populations. We analyzed population-based data of 2,114 children born in Japan in 2010 from the Longitudinal Survey of Babies in the 21st Century, linked to the Perinatal Research Network Database. Comparisons were made between children born by cesarean delivery and those born vaginally. Longitudinal outcomes were atopic dermatitis, food allergy, and bronchial asthma during childhood for each age group up to 9 years of age. We performed Poisson regression analyses with robust variance, and adjusted for child and parent variables, followed by supplementary analyses using generalized estimating equations (GEE). Children born by cesarean delivery did not have a higher risk of most outcomes compared to those born vaginally. GEE analysis found no association between cesarean delivery and atopic dermatitis (adjusted risk ratio [aRR] 0.8, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.5-1.2), food allergy (aRR 1.1, 95% CI 0.7-1.7), bronchial asthma (aRR 1.0, 95% CI 0.8-1.4), or allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (aRR 0.9, 95% CI 0.8-1.1). This study shows no clear evidence of an association between delivery mode and childhood allergic diseases in Japan.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mitselou, N. et al. Cesarean delivery, preterm birth, and risk of food allergy: nationwide Swedish cohort study of more than 1 million children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.142, 1510–1514e2 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Boerma, T. et al. Global epidemiology of use of and disparities in caesarean sections. Lancet392, 1341–1348 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Survey of Medical Institutions (Static/Dynamic Survey) and Hospital Report. (2020). https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/iryosd/20/dl/09gaikyo02.pdf (2020).
-
- Papathoma, E., Triga, M., Fouzas, S. & Dimitriou, G. Cesarean section delivery and development of food allergy and atopic dermatitis in early childhood. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol.27, 419–424 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

