Treatment of Autoimmune Enteropathy With Vedolizumab
- PMID: 40452653
- PMCID: PMC12124378
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001716
Treatment of Autoimmune Enteropathy With Vedolizumab
Abstract
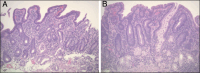
Autoimmune enteropathy (AIE) is a rare condition characterized by immune-mediated villous atrophy with associated chronic diarrhea. In this case, a 34-year-old man with AIE was treated with vedolizumab, an anti-ɑ4b7 integrin that inhibits intestinal lymphocyte trafficking, after initial treatments with prednisone, open-capsule budesonide, azathioprine, infliximab, and adalimumab showed minimal response. Vedolizumab resulted in moderate symptomatic and histological improvement but was discontinued due to possible drug-induced liver injury. This case suggests the potential therapeutic efficacy of vedolizumab in treating AIE, though more research is needed.
Keywords: autoimmune enteropathy; vedolizumab.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
References
-
- Villanacci V, Lougaris V, Ravelli A, et al. Clinical manifestations and gastrointestinal pathology in 40 patients with autoimmune enteropathy. Clin Immunol. 2019;207:10–7. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal S, Raza A, Quigley E. Vedolizumab: A peek into the future of autoimmune enteropathy: 2117. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:S1010–1.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources