Optimized processing and formulation for retaining the sensory and nutritional quality of mustard leaf tea
- PMID: 40452804
- PMCID: PMC12124665
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102515
Optimized processing and formulation for retaining the sensory and nutritional quality of mustard leaf tea
Abstract
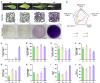
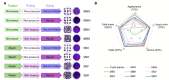
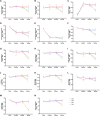
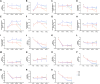
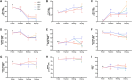
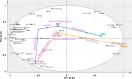
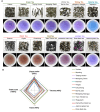
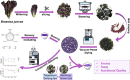
The potential of mustard (Brassica juncea) leaves as a raw material for herbal tea remains unexplored. This study aimed to evaluate the suitability of mustard leaves for tea production and optimize processing and formulation. Four mustard varieties were evaluated using traditional green tea processing techniques, demonstrating that purple-leaf mustard is an excellent raw material for herbal tea, both in terms of sensory properties and bioactive compounds. Next, eight processing methods for purple-leaf mustard were employed. The mustard leaf tea, processed using a combination of steaming fixation, rolling, and vacuum freeze-drying technology, demonstrated effective preservation of health-promoting compounds while maintaining a desirable flavor profile. Blending mustard leaf tea with Maofeng green tea or Tieguanyin oolong tea further enhanced its aroma and taste. This study developed a novel herbal tea using purple-leaf mustard and provides a reference for producing high-quality herbal teas with a unique flavor profile and health-promoting compounds.
Keywords: Blended tea; Brassica juncea; Health-promoting compounds; Herbal tea; Processing technology; Sensory evaluation.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Aoshima H., Hirata S., Ayabe S. Antioxidative and anti-hydrogen peroxide activities of various herbal teas. Food Chemistry. 2007;103(2):617–622.
-
- Castañeda-Ovando A., de Lourdes Pacheco-Hernández M., Páez-Hernández M.E., Rodríguez J.A., Galán-Vidal C.A. Chemical studies of anthocyanins: A review. Food Chemistry. 2009;113(4):859–871. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

