Radiofrequency Controlled Ablation Technique for Arthroscopic Meniscectomy of the Knee
- PMID: 40452989
- PMCID: PMC12126010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2024.103316
Radiofrequency Controlled Ablation Technique for Arthroscopic Meniscectomy of the Knee
Abstract
Despite mixed responses in the literature regarding knee arthroscopies, radiofrequency (RF) ablation remains a preferred method for partial meniscectomy of the knee. This technique is believed to offer advantages over traditional shaving methods, such as reduced risk of long-term fissure propagation and enhanced precision. However, existing literature does not yield a conclusive status of RF's risk-benefit profile, contributing to a mixed response to its recognized utility and safety in the arthroscopic community. This article details a procedure for performing partial meniscectomy with RF ablation using a feedback-controlled bipolar RF device (WEREWOLF FLOW50 Wand; ArthroCare/Smith & Nephew, Austin, TX), with a focus on parameters that can influence intervention safety. These parameters include device-specific factors such as energy transmission type and field density, as well as surgeon-specific factors such as rest/shutoff time, translation speed, and instrumentation depth. Postoperative care typically involves physical therapy, emphasizing early mobilization and strengthening exercises to ensure optimal recovery. Although our clinic has observed positive results with feedback-controlled bipolar RF for partial meniscectomy, further studies are necessary to conclusively determine the risk-benefit profile of this technique, including long-term follow-up to assess durability and patient satisfaction. Additionally, comparisons with other techniques could provide a more comprehensive understanding of its efficacy and overall impact on patient outcomes.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: C.M. reports that financial support was provided by Smith & Nephew; reports a consulting or advisory relationship with Smith & Nephew; and receives speaking and lecture fees and travel reimbursement from Smith & Nephew. Both other authors (A.C., C..B.) declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


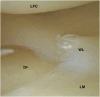


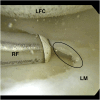

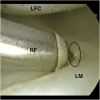
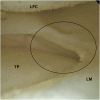
References
-
- Stalder K.R., McMillen D.F., Woloszko J. Electrosurgical plasmas. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2005;38:1728–1738.
-
- Allen R.T., Tasto J.P., Cummings J., Robertson C.M., Amiel D. Meniscal debridement with an arthroscopic radiofrequency wand versus an arthroscopic shaver: Comparative effects on menisci and underlying articular cartilage. Arthroscopy. 2006;22:385–393. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

