Metabolic reprogramming in viral infections: the interplay of glucose metabolism and immune responses
- PMID: 40453076
- PMCID: PMC12122472
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1578202
Metabolic reprogramming in viral infections: the interplay of glucose metabolism and immune responses
Abstract
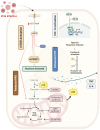
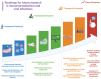
Metabolic reprogramming is an important player within the immune response to viral infections, allowing immune cells to fine-tune their energy production and biosynthetic requirements while it is actively working to restrict pathogen access to essential nutrients. Particularly, glucose metabolism, which appears to be one of the important regulators of immune function, affects immune cell activation, cytokine secretion, and pathogen restriction. This review explores the mechanisms of metabolic reprogramming during viral infections, with a specific emphasis on glucose metabolism. We discussed the key cytokines involved in orchestrating this metabolic process and the influence of pre-existing metabolic disorders on immune efficiency. Furthermore, we introduced emerging therapeutic strategies that target glucose metabolism to enhance antiviral immunity and improve disease outcomes. A deeper understanding of the interaction between metabolism and immunity could be promising for the development of novel immunometabolic targets against viral infections.
Keywords: cytokines; diabetes; glucose metabolism; immune activation; immunometabolism; pathogen clearance; viral infections.
Copyright © 2025 Darweesh, Mohammadi, Rahmati, Al-Hamadani and Al-Harrasi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

