Single-cell multi-omics reveals the TNF-α activation threshold for Classical Monocytes by studying healthy donors and rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 40453083
- PMCID: PMC12122427
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1572823
Single-cell multi-omics reveals the TNF-α activation threshold for Classical Monocytes by studying healthy donors and rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
Introduction: Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha is a known pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a key role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-cytokine therapies targeting Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha have greatly succeeded in treating rheumatoid arthritis in many patients. Despite these developments, many of the mechanisms of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha action have yet to be uncovered.
Methods: In this study, we incubated PBMCs from healthy donors and rheumatoid arthritis patients with Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and then performed their single-cell multi-omics analysis via BD Rhapsody.
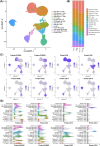
Results: We have observed that Classical Monocytes have responded to the Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha stimulation the most and that there was an activational threshold for such response that was dependent on the TNFR2 protein expression level.
Discussion: The profiling of TNFR2 protein expression level on immune cell populations can be a good predictive factor for the assessment of their activation by Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha.
Keywords: CITE-seq; ScRNA-seq; TNF-α; TNFR1; TNFR2; response to TNF-α; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2025 Perik-Zavodskii, Perik-Zavodskaia, Alrhmoun, Lopatnikova, Alshevskaya, Zhukova, Shevchenko, Shkaruba, Sivitskaya, Suleimanov, Sheveleva, Nazarov, Kireev, Sizikov, Golikova and Sennikov.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ashiq K, Ashiq S, Mobashar A, Abid F, Yasmeen A, Shehzadi N, et al. . An updated review on rheumatoid arthritis (RA): epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and the current approaches for its treatment. Sudan J Med Sci (SJMS). (2023) 29:539–51. doi: 10.18502/sjms.v18i4.14742 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

