Novel insights into the crosstalk between non-coding RNA and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic functions and therapeutic applications
- PMID: 40453089
- PMCID: PMC12122316
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550839
Novel insights into the crosstalk between non-coding RNA and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic functions and therapeutic applications
Abstract
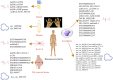
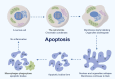
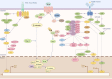
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder and a leading cause of disability worldwide, significantly impairing patients' quality of life. As current therapeutic options remain limited, there is an urgent need for novel strategies, including the use of medicinal plants, to delay the development and progression of RA. Acute inflammation in RA is often accompanied by impaired apoptosis, which contributes to disease pathogenesis. With advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies, an increasing number of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been identified and extensively studied for their roles in both physiological and pathological processes. Dysregulation of these ncRNAs-particularly long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs)-has been implicated in various disorders, including RA. Given the well-established association between apoptosis and ncRNA expression in RA, a comprehensive understanding of their intricate interplay is essential. In this study, we systematically explore the complex interactions between lncRNAs and circRNAs in regulating apoptosis during the pathogenesis of RA. Additionally, we highlight emerging evidence, suggesting that ncRNA-mediated modulation of apoptosis can be achieved through herbal medicines, offering promising therapeutic avenues for RA treatment.
Keywords: TCM; apoptosis; ncRNAs; rheumatoid arthritis; therapeutic applications.
Copyright © 2025 Wen, Liu, Wan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Machin AR, Babatunde O, Haththotuwa R, Scott I, Blagojevic-Bucknall M, Corp N, et al. . The association between anxiety and disease activity and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 39:1471–82. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04900-y - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

