Enhancing detection and monitoring of circulating tumor cells: Integrative approaches in liquid biopsy advances
- PMID: 40453103
- PMCID: PMC12124603
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100297
Enhancing detection and monitoring of circulating tumor cells: Integrative approaches in liquid biopsy advances
Abstract
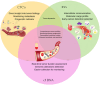
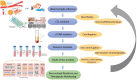
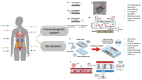
Liquid biopsy offers a minimally invasive method for detecting and monitoring cancer, with key biomarkers including circulating tumor cells (CTCs), cell-free DNA (cfDNA), and extracellular vesicles (EVs). Among these, CTCs provide dynamic insights into tumor heterogeneity, metastatic potential, and therapeutic resistance through molecular profiling and single-cell analysis. This review examines recent advancements in technologies such as microfluidics, nanotechnology, and next-generation sequencing (NGS), which have improved the accuracy and clinical use of CTC detection. A comparative analysis of liquid biopsy techniques highlights the strengths and limitations of key platforms, including NGS, digital PCR (ddPCR), and quantitative PCR (qPCR), providing insights into diagnostic accuracy and clinical significance. Combining genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic analyses with artificial intelligence (AI) tools has enhanced tumor profiling and supports personalized treatment decisions in precision oncology. Despite notable progress, issues like assay standardization, sample variability, regulatory complexity, and data integration still limit widespread clinical use. Future directions emphasize interdisciplinary innovation, clinical validation, and robust bioinformatics frameworks to facilitate the seamless incorporation of CTC-based liquid biopsy into standard oncology practice. Overcoming these challenges may allow liquid biopsy to become a standard tool for early cancer detection, ongoing monitoring, and individualized treatment.
Keywords: Cell-free DNA; Circulating tumor cells; Exosomes; Liquid biopsy; Nanotechnology; Next-generation sequencing.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of liquid biopsy in breast cancer: Redefining the landscape of non-invasive precision oncology.J Liq Biopsy. 2025 May 21;8:100299. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100299. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Liq Biopsy. 2025. PMID: 40521566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic-based technologies in cancer liquid biopsy: Unveiling the role of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) materials.Environ Res. 2023 Dec 1;238(Pt 1):117083. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117083. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37690629 Review.
-
Circulating Liquid Biopsy Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: Advances and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7974. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147974. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A comprehensive review of techniques, applications, and future prospects.Kidney Cancer. 2024 Feb;8(1):205-225. doi: 10.1177/24684570241303346. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Kidney Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39886007 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy: current technology and clinical applications.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Sep 12;15(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01351-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36096847 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liquid Biopsy: Current advancements in clinical practice for bladder cancer.J Liq Biopsy. 2025 Jul 8;9:100310. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100310. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Liq Biopsy. 2025. PMID: 40698358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking glioblastoma: breakthroughs in molecular mechanisms and next-generation therapies.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 21;42(7):276. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02830-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40542948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy in breast cancer: clinical implications of ctDNA and CTCs in diagnosis, treatment and monitoring.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05343-7. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40586858 Review.
-
Role of Liquid Biopsy for Early Detection, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Monitoring of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 28;15(13):1655. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15131655. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647654 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gerratana L., Davis A.A., Foffano L., Reduzzi C., Rossi T., Medford A.…Cristofanilli M. Integrating Machine Learning-Predicted Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in Metastatic Breast Cancer: a proof of principle study on endocrine resistance profiling. Cancer Lett. 2024 - PubMed
-
- Dai Y., He J., Zhou Y., Yu Y., Hui H., Guo L., Yin H. Constructing a highly sensitive duplex immunoassay using AuNPs and AgNPs as nanolabels for investigating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition occurring on circulating tumor cells with lung cancer patients. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025;270 - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto D.T., Sequist L.V., Lee R.J. Circulating tumour cells—monitoring treatment response in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014;11(7):401–412. - PubMed
-
- Viswanath B., Kim S. Recent insights into the development of nanotechnology to detect circulating tumor cells. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. 2016;82:191–198.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

