The Silver Agri Age project in Italy: a Montessori-inspired social intervention with older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Single-group pre-post pilot study protocol
- PMID: 40453497
- PMCID: PMC12122297
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1561263
The Silver Agri Age project in Italy: a Montessori-inspired social intervention with older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Single-group pre-post pilot study protocol
Abstract
Introduction: According to literature, an estimated percentage of 10-15% of people diagnosed with Mild Cognitive Impairment each year develop Alzheimer's dementia. Prevention and non-pharmacological treatments play an important role in dealing with this emergency. In this regard, literature has highlighted how exposure to nature, participation in horticultural and cognitive activities, and adopting a Montessori approach are useful to counteract cognitive decline and promote well-being. Therefore, the Silver Agri Age pilot study will test a Montessori-inspired social intervention that will be carried out on farms of the Marche Region (Central Italy) authorized for social agriculture and aimed at an older adult population with mild cognitive impairment in order to improve their well-being and quality of life. This paper describes the pilot study protocol and main outcome.
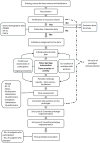
Methods: Four older adult people will be involved for each of the three farms participating in the study, for a total of 12 participants. The inclusion criteria will be age ≥ 55, Mini-Mental State Examination ≥ 24, ability and willingness to sign informed consent. The evaluation will focus on the assessment of the person's emotional well-being, life quality, and cognitive status. To evaluate the feasibility of the pilot project, the quality of participants' engagement in the activities and the satisfaction of the subjects and their caregivers with the project will also be assessed.
Discussion and conclusion: During each three-month phase of the project different social farming activities will be proposed. Activities will also include sensory and cognitive stimulation and socialization within the farm. Since according to literature, participation in Montessori-based programs and exposure to nature generate positive effects, the emotional well-being of participants will be assessed as a primary outcome and life quality as a secondary outcome. Additionally, we believe that promoting participation in progressively challenging activities and autonomy may help stabilize cognitive decline. Therefore, cognitive level will also be assessed as a secondary outcome. Ultimately, the pilot study will provide insights into the possibility of integrating a prototype non-pharmacological intervention aimed at improving the well-being and quality of life of people with MCI into the dementia prevention service system.
Clinical trial: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06754202.
Keywords: Montessori; mild cognitive impairment; nature; psychosocial intervention; social farming.
Copyright © 2025 Gambella, Lombardi, Cicconi, Raccichini, Paciaroni, Giuli, Bonfigli, Fabbietti, Pelliccioni and Gagliardi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Prince MJ, Wimo A, Guerchet MM, Ali GC, Wu Y-T, Prina M. World Alzheimer report 2015. The global impact of dementia: an analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. [Research report] Alzheimer's disease international, the global voice in dementia. London: University of Cambridge Research; (2015).
-
- Caffò AO, Spano G, Tinella L, Lopez A, Ricciardi E, Stasolla F, et al. The prevalence of amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment and its association with different lifestyle factors in a south Italian elderly population. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:3097. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19053097, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical