Angiogenesis in rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathological characterization, pathogenic mechanisms, and nano-targeted therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 40453697
- PMCID: PMC12124647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.04.026
Angiogenesis in rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathological characterization, pathogenic mechanisms, and nano-targeted therapeutic strategies
Abstract
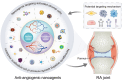
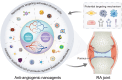
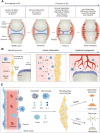
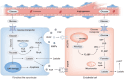
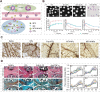
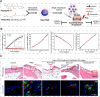
Angiogenesis is critical from early development through the progression of life-threatening diseases. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), angiogenesis is markedly heightened and undergoes aberrant changes that exacerbate the progression of synovitis. However, the intricate mechanisms underlying these changes remain poorly understood. Despite the development of numerous anti-angiogenic agents, their clinical efficacy is often compromised by adverse effects and the emergence of adaptive resistance, leading to disease relapse or progression. Nanomedicine has gained significant attention owing to its excellent biocompatibility, precise biological targeting, and enhanced therapeutic outcomes. Anti-angiogenic nanoagents have shown transformative potential in treating cancer and retinal diseases. Nevertheless, a comprehensive review addressing the fundamental mechanisms of anti-angiogenic nanoagents in RA has yet to be undertaken. Herein, this review provides an in-depth description of the unique structural and functional aspects of pathological angiogenesis in RA and its negative consequences. The mechanisms of pro-angiogenic mediators contributing to RA angiogenesis are further explored. Subsequently, biological activities of nanomedicines for the treatment of RA are summarized. Finally, the cutting-edge developments in the anti-angiogenic nanoagents of RA engineered based on these mechanisms and bioactivities are outlined. A helpful introduction to anti-angiogenic strategies for treatment of RA, which may offer novel perspectives for the development of nanoagents, is opening a new horizon in the fight against RA.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Nanoagents; Pro-angiogenic factor; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures











References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

