Treatment of hypothyroidism with the combination of levothyroxine and slow-release triiodothyronine: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 40453773
- PMCID: PMC12123354
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcte.2025.100395
Treatment of hypothyroidism with the combination of levothyroxine and slow-release triiodothyronine: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Some patients with hypothyroidism lack satisfaction with levothyroxine (LT4) monotherapy, which may be related to lower serum triiodothyronine (T3) and T3/T4 ratios compared to control individuals. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a combination therapy of slow-release T3 (SRT3) and LT4 in patients with primary hypothyroidism compared with LT4 monotherapy.
Methods: Thirty-two hypothyroid women were randomized into two groups of SRT3 + LT4 combination and LT4 monotherapy. Group one received a combination of 15 µg SRT3 and 75 µg LT4, and group two received 100 µg LT4 daily for 8 weeks. Clinical and biochemical measurements were performed at baseline and 4 to 8 weeks after intervention.
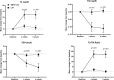
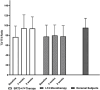
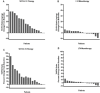
Results: There were no significant changes in serum levels of fT4, T3, TSH, and T3/fT4 ratio in the LT4 group at the end of 4 to 8 weeks of study. A statistically significant decrease in fT4 and TSH, and an increase in serum T3 and the T3/fT4 ratio, were observed in the SRT3 + LT4 group. The T3/fT4 ratio reached comparable values to those in normal subjects, 93.63 ± 23.25 vs 95.06 ± 19.44 ng/ng, respectively. The rise in the T3/fT4 ratio 8 weeks after SRT3 + LT4 treatment was between 21 % and 90 % in 10 patients and 1 % and 13 % in 5 patients, with no change in one patient.
Conclusion: The novel combination of SRT3 + LT4 therapy resulted in a significant increase in serum T3 and the T3/fT4 ratio in hypothyroid patients compared to those receiving LT4 monotherapy. The rise in the T3/fT4 ratio was ≥ 21 % in two-thirds of patients; the lack of a significant increase in the T3/fT4 ratio in some patients during SRT3-LT4 combination therapy demands further investigation.
Keywords: Hypothyroidism; Levothyroxine; Slow-release; Triiodothyronine.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Jonklaas J., Bianco A.C., Bauer A.J., Burman K.D., Cappola A.R., Celi F.S., et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the american thyroid association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid : official journal of the American Thyroid Association. 2014;24(12):1670–1751. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saravanan P., Chau W.-F., Roberts N., Vedhara K., Greenwood R., Dayan C.M. Psychological well-being in patients on ‘adequate’ doses of l-thyroxine: results of a large, controlled community-based questionnaire study. Clin Endocrinol. 2002;57(5):577–585. - PubMed
-
- Wekking E.M., Appelhof B.C., Fliers E., Schene A.H., Huyser J., Tijssen J.G., et al. Cognitive functioning and well-being in euthyroid patients on thyroxine replacement therapy for primary hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005;153(6):747–753. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

