Prevalence of Chikungunya, Dengue, and West Nile arboviruses in Iran based on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40453908
- PMCID: PMC12123324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gloepi.2025.100202
Prevalence of Chikungunya, Dengue, and West Nile arboviruses in Iran based on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Arboviruses, including Chikungunya (CHIKV), Dengue (DENV), and West Nile (WNV) viruses, are significant viral threats that affect numerous people globally each year. This report explores the prevalence of these viruses in Iran through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
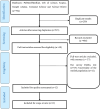
Methods: The present survey was performed using a systematic review and meta-analysis method on the seroprevalence of WNV, CHIKV, and DENV using the ELISA test. Accordingly, by searching Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Science Direct, and Google Scholar scientific databases, all relevant published papers were sorted out and reviewed. Power ratification of data was conducted with a random effects model in meta-analysis, meta-regression, I 2 index, and Egger test.
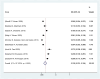
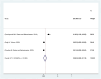
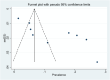
Results: This meta-analysis report embodies twelve published papers between 2000 and 2024. The seroprevalence of positive ELISA tests for WNV in Iran was estimated at 12.9 % (CI = 95 %: 7.4-18.4) and for CHIKV at 6.2 % (CI = 95 %: 0.6-11.8). Regarding DENV, only two studies were conducted, with a zero prevalence in one study and a seroprevalence of 5.6 % in another study.
Conclusion: According to these data, WNV, CHIKV, and DENV fevers have been detected in Iran using the ELISA test. Considering the seropositivity of WNV and CHIKV and their detection in several provinces, it can be assumed that these viruses are ubiquitous, while DENV fever remains sporadic in Iran.
Keywords: Arbovirus; Chikungunya; Dengue; ELISA; Meta-analysis; Virus; WNV.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
Further reading
-
- Moirano G., Richiardi L., Calzolari M., Merletti F., Maule M. Recent rapid changes in the spatio-temporal distribution of West Nile neuro-invasive disease in Italy. Zoonoses Public Health. 2020;67(1):54–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

