Optimization of RfxCas13d Expression in Escherichia coli Host using Response Surface Methodology
- PMID: 40453911
- PMCID: PMC12123183
- DOI: 10.18502/ajmb.v17i2.18563
Optimization of RfxCas13d Expression in Escherichia coli Host using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
Background: RfxCas13d, a key member of the Cas13 family, plays a vital role in CRISPR-based diagnostics for RNA sequence detection and gene silencing. This study aimed to enhance RfxCas13d expression by optimizing key parameters using Response Surface Methodology (RSM).
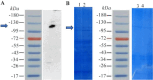
Methods: The plasmid pET28b-RfxCas13d-His (Addgene 141322) was introduced into BL21 (DE3) and Rosetta™ (DE3) strains. Initial expression tests were conducted, followed by RSM-guided optimization of factors such as isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) concentration, temperature, cell density at induction, and induction time in BL21 (DE3). Protein expression levels were quantified using ImageJ and AlphaEaseFC software to analyze band intensities.
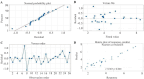
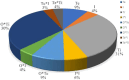
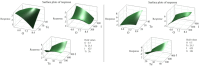
Results: BL21 (DE3) was selected for further optimization based on preliminary results. Analysis of 26 RSM-designed experiments revealed that temperature, induction time, IPTG concentration, and their interactions significantly influenced RfxCas13d expression. Optimal conditions were identified as 0.25 mM IPTG, an OD600 nm of 0.8 at induction, 37°C, and Overnight (ON) of induction. The regression model exhibited high accuracy, with a correlation coefficient of 0.97 and a p-value less than 0.05, confirming a strong linear relationship between predicted and observed values.
Conclusion: This study highlights the significant impact of the four optimized factors on RfxCas13d expression. Under optimized conditions, a soluble protein concentration of 3.6 mg/100 ml cell culture was achieved after purification. It represents the first application of RSM for optimizing RfxCas13d expression, providing a foundation for further refinement of expression conditions. Continued use of RSM in future research will enhance the efficiency of RfxCas13d production for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Base sequence; CRISPR-associated proteins; Escherichia coli; Protein biosynthesis.
Copyright© 2025 Avicenna Journal of Medical Biotechnology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Optimization of the Expression of DT386-BR2 Fusion Protein in Escherichia coli using Response Surface Methodology.Adv Biomed Res. 2017 Mar 1;6:22. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.201334. eCollection 2017. Adv Biomed Res. 2017. PMID: 28349025 Free PMC article.
-
Using response surface methodology in combination with Plackett-Burman design for optimization of culture media and extracellular expression of Trichoderma reesei synthetic endoglucanase II in Escherichia coli.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Oct;45(5):1197-1208. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4272-y. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30032381
-
Enhanced Biomass Production of Recombinant Pfu DNA Polymerase Producer Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by Optimization of Induction Variables Using Response Surface Methodology.Protein J. 2023 Aug;42(4):451-462. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10122-8. Epub 2023 May 18. Protein J. 2023. PMID: 37199865
-
Optimization of culture conditions for Mpt64 synthetic gene expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) using surface response methodology.Heliyon. 2019 Nov 28;5(11):e02741. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02741. eCollection 2019 Nov. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31844694 Free PMC article.
-
5-Aminolevulinate production with recombinant Escherichia coli using a rare codon optimizer host strain.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Jun;75(4):777-82. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-0887-y. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17333171
References
-
- Pardee K, Green AA, Takahashi MK, Braff D, Lambert G, Lee JW, et al. Rapid, low-cost detection of Zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell 2016;165(5):1255–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
