A bibliometric analysis of the frontiers and hotspots in chronic endometritis
- PMID: 40454156
- PMCID: PMC12122336
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1559543
A bibliometric analysis of the frontiers and hotspots in chronic endometritis
Abstract
Background: Chronic endometritis (CE) is an inflammatory condition characterized by endometrial plasmacyte infiltration. The diagnosis and treatment of CE have attracted more and more attention. This article aimed to analyze the relevant keywords, development trends, and research hotspots of CE, which can provide a direction for future research.
Materials and methods: The relevant articles on CE were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. VOSviewer and CiteSpase were applied to analyze publication years, countries, institutions, journals, authors, citation and co-citation, co-occurrence and citation burst of keywords.
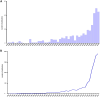
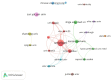
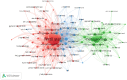
Results: A total of 373 publications on CE were retrieved. Annual publication of articles about CE grew rapidly, and 2022 had the biggest outputs (50). USA contributed the most publications (87), and the University of Bari Aldo Moro had the highest number of articles in this field (27). The journal with the highest cited count and most publications was Fertility and Sterility (30). The main disciplines concerning the research on CE were Obstetrics Gynecology (141, 38.11%) and Reproductive Biology (126, 34.05%). Ettore Cicinelli, Kotaro Kitaya, and Dominique De Ziegler were the top three authors in publications. Except for CE and endometritis, the five most common keywords were infertility, hysteroscopy, plasma cell, recurrent implantation failure, and CD138. Pregnancy loss and recurrent miscarriage are currently within the burst period and might be the persistent research heated topics in this field.
Conclusion: This study is useful for researchers to quickly grasp the current situation of CE research and enlighten researchers to explore new problems in CE.
Keywords: CD138; bibliometric analysis; chronic endometritis; infertility; pregnancy loss.
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Huang, Li, Yang and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Global research on NK cells in miscarriage: a bibliometric study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 17;12:1513213. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1513213. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40034381 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends in endometrial receptivity from 2000 to 2024: bibliometric analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 30;11:1465893. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1465893. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39540052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric analysis of global research on vitamin D and reproductive health between 2012 and 2021: Learning from the past, planning for the future.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 8;9:973332. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.973332. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36159484 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives and trends of CD39-CD73-eAdo/A2aR research in tumor microenvironment: a bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1427380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427380. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39188712 Free PMC article.
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
References
-
- Michels TC. Chronic endometritis. Am Fam Physician. (1995) 52:217–22. - PubMed
-
- Kiviat NB, Wolnerhanssen P, Eschenbach DA, Wasserheit JN, Paavonen JA, Bell TA, et al. . Endometrial histopathology in patients with culture-proved upper genital-tract infection and laparoscopically diagnosed acute salpingitis. Am J Surg Pathol. (1990) 14:167–75. 10.1097/00000478-199002000-00008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cicinelli E, Matteo M, Tinelli R, Pinto V, Marinaccio M, Indraccolo U, et al. . Chronic endometritis due to common bacteria is prevalent in women with recurrent miscarriage as confirmed by improved pregnancy outcome after antibiotic treatment. Reprod Sci. (2014) 21:640–7. 10.1177/1933719113508817 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

