Tocilizumab-Based Treatment of Microvascular Inflammation in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 40454296
- PMCID: PMC12124137
- DOI: 10.3389/ti.2025.14502
Tocilizumab-Based Treatment of Microvascular Inflammation in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
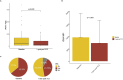
Chronic-active antibody mediated rejection (caAMR) is the leading causes of long-term kidney graft failure. Tocilizumab (TCZ), an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, has been suggested as a treatment, but data are conflicting. We retrospectively studied consecutive adult kidney transplant recipients with caAMR or microvascular inflammation (MVI) without Donor-Specific Antibodies (DSA) and without C4d deposition (MVI + DSA-C4d-), who received TCZ as first-line therapy in two European centers. Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and DSA were assessed one-year before and after TCZ initiation. The study included 64 patients who received TCZ between July 2018 and September 2023. The eGFR trajectory significantly decreased after TCZ treatment (-1.2 ± 0.2 vs. 0.03 ± 0.2 mL/min/1.73 m2/month pre- vs. post-TCZ, respectively; p = 0.001). The percentage of patients with DSA decreased from 63.9% to 38.9% (p < 0.001), and the average MFI decreased from 9,537 to 7,250 (p = 0.001). In multivariate analysis, younger age (OR = 0.95, p = 0.02), MVI + DSA-C4d- phenotype (OR = 5.2, p = 0.01), and lower chronic glomerulopathy score (OR = 4.5, p = 0.02) were associated with TCZ response (trajectory ≥0 after TCZ). Patient survival was 98.4%, and graft survival was 93.7% at one-year. First-line TCZ therapy for caAMR or MVI + DSA-C4d- is associated with an improvement of eGFR trajectories, reduced DSA numbers and MFI and histological inflammation in glomeruli. These data suggest a potential benefit of TCZ in these settings.
Keywords: chronic-active antibody-mediated rejection; donor-specific antibody; kidney transplantation; microvascular inflammation; tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2025 Noble, Comai, Corredetti, Laamech, Dard, Jouve, Giovannini, Le Gouellec, Wadnerkar, Cravedi, Apuzzo, Vetrano, Busutti, Abenavoli, Malvezzi, Rostaing and Lamanna.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

