Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Lifileucel Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Cell Therapy in Patients With Advanced Melanoma: A 5-Year Analysis of the C-144-01 Study
- PMID: 40454684
- PMCID: PMC12622280
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-25-00765
Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Lifileucel Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Cell Therapy in Patients With Advanced Melanoma: A 5-Year Analysis of the C-144-01 Study
Abstract
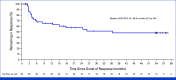
Patients with advanced melanoma resistant to immune checkpoint or BRAF/MEK inhibitors have treatment options with relatively low efficacy. Lifileucel, a one-time autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte cell therapy, was approved in the United States on the basis of the pivotal C-144-01 study. A 5-year follow-up of the C-144-01 trial assessed the long-term efficacy and safety of lifileucel. At the cutoff date (November 20, 2024), the objective response rate was 31.4% (complete response [CR], 5.9%; partial response [PR], 25.5%). Overall, 79.3% of patients had tumor burden reduction; 16 had deepened responses with four converting from PR to CR > 1 year after lifileucel infusion; 31.3% of responders completed the 5-year assessment with ongoing responses. The median duration of response was 36.5 months. Responders (n = 48) had lower tumor burden and fewer liver or brain metastases than the overall population. The median overall survival (OS) was 13.9 months, with a 5-year OS of 19.7%. Adverse events were consistent with nonmyeloablative lymphodepletion and interleukin-2 safety profiles and declined rapidly within 2 weeks after lifileucel infusion. Most grade 3/4 cytopenias resolved to grade ≤2 by day 30. This 5-year analysis demonstrated long-term benefit and meaningful OS with one-time lifileucel therapy, with no additional long-term safety concerns.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures


References
-
- Ribas A, Hamid O, Daud A, et al. Association of pembrolizumab with tumor response and survival among patients with advanced melanoma. JAMA. 2016;315:1600–1609. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Grob JJ, Stroyakovskiy D, et al. Five-year outcomes with dabrafenib plus trametinib in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:626–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

