A new naphthalene-based fluorogenic substrate for cytochrome P450 4A11
- PMID: 40454940
- PMCID: PMC12191924
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20253130
A new naphthalene-based fluorogenic substrate for cytochrome P450 4A11
Abstract
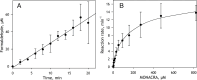
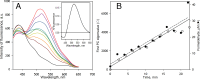
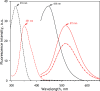
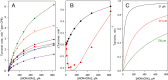
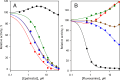
We aimed to create a high-throughput fluorimetric assay for the activity of CYP4A11, the major 20-HETE-producing enzyme. To this end, we probed 3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)acrylic acid (MONACRA) as a potential CYP4A11 substrate. We studied its metabolism using human liver microsomes (HLM) and recombinant P450 enzymes. O-demethylation of MONACRA by cytochromes P450 creates 3-(6-hydroxynaphthalen-2-yl)acrylic acid. The bright fluorescence of the product and its clear spectral resolution from the substrate allowed us to create a fluorimetric assay of MONACRA metabolism. We tested 16 recombinant human P450 enzymes and found noticeable demethylation activity only with CYP4A11 and CYP1A2. The KM for CYP4A11 is 189±37 μM, and the kcat accounts for 67±18 min-1. CYP1A2 exhibits a KM of 161±34 μM, with a kcat value of 44±6 min-1, although this enzyme also exhibited a decreased rate of turnover at high substrate concentrations, evidencing substrate inhibition with Ksi=650±200 μM. The studies with fluvoxamine and epalrestat, specific inhibitors of CYP1A2 and CYP4A11, respectively, showed that despite the activity of recombinant CYP1A2 with MONACRA, it does not take part in its metabolism in HLM. Thus, MONACRA can be utilized as a specific fluorogenic substrate of CYP4A11. We developed a robust and sensitive automated fluorimetric assay of MONACRA demethylation and used it to compare the substrate saturation profiles in seven pooled HLM preparations with the known composition of the P450 pool. These studies demonstrated a close correlation between the rate of the main kinetic phase of MONACRA metabolism and the fractional content of CYP4A11 in the P450 pool.
Keywords: 3-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)acrylic acid; CYP1A2; CYP4A11; fluorogenic substrates; high-throughput activity assay; human liver microsomes.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

