Arginine promotes the activation of human lung fibroblasts independent of its metabolism
- PMID: 40454944
- PMCID: PMC12235046
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20253033
Arginine promotes the activation of human lung fibroblasts independent of its metabolism
Abstract
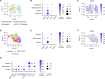
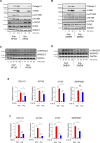
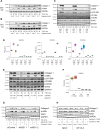
Arginine is a conditionally essential amino acid with known roles in protein production, nitric oxide synthesis, biosynthesis of proline and polyamines, and regulation of intracellular signaling pathways. Arginine biosynthesis and catabolism have been linked to transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-induced activation of fibroblasts in the context of pulmonary fibrosis; however, a thorough study on the metabolic and signaling roles of arginine in the process of fibroblast activation has not been conducted. Here, we examined the role and regulation of arginine metabolism in lung fibroblasts activated with TGF-β. We found that TGF-β increases the expression of arginine biosynthetic and catabolic enzymes in lung fibroblasts. Surprisingly, using metabolic tracers of arginine and its precursors, we found little evidence of arginine synthesis or catabolism in lung fibroblasts treated with TGF-β. Despite this, arginine remained crucial for TGF-β-induced expression of collagen and α-smooth muscle actin. We found that arginine limitation leads to the activation of general control nonderepressible 2 (GCN2), while inhibiting TGF-β-induced mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 activation and collagen protein production. Extracellular citrulline could rescue the effect of arginine deprivation in an argininosuccinate synthase-dependent manner. Our findings suggest that the major role of arginine in lung fibroblasts is for charging of arginyl-tRNAs and promotion of signaling events which are required for fibroblast activation.
Keywords: arginine; fibroblast; metabolism; pulmonary fibrosis; transforming growth factor-β.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Role of Arginine and its Metabolism in TGF-β-Induced Activation of Lung Fibroblasts.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 1:2024.11.01.618293. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.01.618293. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biochem J. 2025 Jun 17;482(12):BCJ20253033. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20253033. PMID: 39554075 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

