Assessment of maternal health and behavior during pregnancy in the HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study: Rationale and approach
- PMID: 40455057
- PMCID: PMC11743802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101494
Assessment of maternal health and behavior during pregnancy in the HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study: Rationale and approach
Abstract
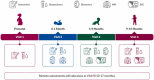
The Healthy Brain and Child Development (HBCD) Study, a multi-site, prospective, longitudinal cohort study, will examine human brain, cognitive, behavioral, social, and emotional development beginning prenatally and planned through early childhood. Prenatal exposures, including substances of abuse, impact fetal development and have effects across the life course. During the development of the HBCD Study, the Pregnancy Exposures, Including Substances Workgroup (WG-PRG) was charged with characterizing maternal health and behavior during pregnancy into the childhood years. Maternal physical and mental health, including substance use, and pregnancy and birth complications and outcomes were prioritized. Pregnancy, chronic and acute health conditions, family mental health, and healthcare utilization were assessed using existing and novel measures. Maternal mental health was assessed with the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale, select items in the DSM-5 Self-Rated Level-1 and -2 Cross-Cutting Symptom Measures, and the National Stressful Events Survey-PTSD Short Scale. Finally, participants reported lifetime, recent, and current use of substances using a modified-ASSIST during pregnancy and postpartum. Quantities and frequencies of reported substances were collected for select periods prior to and during pregnancy through an interview (or web application) using the timeline-followback method. HBCD will advance our understanding of the impact of the intrauterine environment on early development.
Keywords: Brain; Child development; HBCD; Maternal health; Pregnancy; Prenatal exposure delayed effects; Substance-related disorders.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing prenatal and early childhood social and environmental determinants of health in the HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study (HBCD).Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Oct;69:101429. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101429. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39208687 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal exposure to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis and birth, growth, and social-emotional developmental outcomes throughout early childhood in Kenya: a prospective cohort study.Lancet Glob Health. 2025 Mar;13(3):e467-e478. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(24)00471-6. Lancet Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40021305 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An introduction to the HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study (HBCD) study.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Oct;69:101441. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101441. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39293188 Free PMC article.
-
The Perinatal Committee report: Review of the progress of obstetric healthcare in Japan.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2025 Jul;51(7):e16354. doi: 10.1111/jog.16354. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2025. PMID: 40690975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substance exposure in utero and developmental consequences in adolescence: a systematic review.Child Neuropsychol. 2012;18(6):521-49. doi: 10.1080/09297049.2011.628309. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Child Neuropsychol. 2012. PMID: 22114955
References
-
- All of Us Survey Explorer. n.d.. Retrieved February 12, 2024, from 〈https://www.researchallofus.org/data-tools/survey-explorer/〉.
-
- Anunziata F., Cisneros C., Natale Castillo M.I., Perez A., Rodriguez V., De La Cruz S., Estrada K., Durbal A., Jaramillo M., Enriquez Marquez L., Nuñez J., Peralta-Carcelen M., Lee Wisnowski J. ¿Donde están? Hispanic/Latine inclusion, diversity and representation in the HEALthy Brain and Child Development Study (HBCD). Developmentla Cognitive Neuroscience, 70, 101477. 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101477. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DA055349/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055369/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055355/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055361/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA055325/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055358 /DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055344/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055338/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055316/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA050700/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055322/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055354/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055363 /DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055360/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055359/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055367/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055366 /DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055350/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055347/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055352/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055370/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055357/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055366/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA055330/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055371/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055342/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055353/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055365/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA055362/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical