Flavonoid Stability and Biotransformation in Agricultural Soils: Effects of Hydroxylation, Methoxylation, and Glycosylation
- PMID: 40455566
- PMCID: PMC12164328
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c02814
Flavonoid Stability and Biotransformation in Agricultural Soils: Effects of Hydroxylation, Methoxylation, and Glycosylation
Abstract
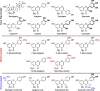
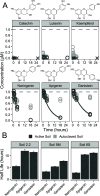
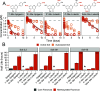
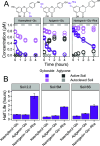
Stricter pesticide regulations are increasing the demand for environmentally acceptable alternatives with flavonoids seen as promising candidates for use as biopesticides. However, the current limited understanding of the environmental fate of flavonoids in soils restricts their assessment as active pesticide ingredients. To address this knowledge gap, we conducted laboratory incubation experiments with LC-MS-based quantification to determine the half-lives of 18 structurally related flavonoids in three agricultural soils. Hydroxylated flavonoids were rapidly transformed (t1/2: 3-12 h), while methoxylated derivatives exhibited substantially longer half-lives, which increased with the number of methoxy groups (t1/2: 5-460 h). Glycosylated flavonoids were primarily transformed into their aglycones (t1/2: 0.5-5 h). Incubation experiments with autoclaved soil indicated that biotic processes primarily catalyzed the observed transformations. All trends were consistent across different soil types and pH values. This study provides a comprehensive overview of flavonoid stability in agricultural soils, enhancing our understanding of their potential as alternative pesticides.
Keywords: biopesticide; soil half-life; structure−stability relationship; sustainable agriculture.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eawag-Soil in enviPath: a new resource for exploring regulatory pesticide soil biodegradation pathways and half-life data.Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2017 Mar 22;19(3):449-464. doi: 10.1039/c6em00697c. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2017. PMID: 28229138
-
Characterization of adsorption and degradation of diuron in carbonatic and noncarbonatic soils.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Jan 27;58(2):1055-61. doi: 10.1021/jf902792p. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20047273
-
Effect of different organic amendments on the dissipation of linuron, diazinon and myclobutanil in an agricultural soil incubated for different time periods.Sci Total Environ. 2014 Apr 1;476-477:611-21. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.052. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Sci Total Environ. 2014. PMID: 24496034
-
Advances on the in vivo and in vitro glycosylations of flavonoids.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Aug;104(15):6587-6600. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10667-z. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32514754 Review.
-
Advances in the biotechnological glycosylation of valuable flavonoids.Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Nov 1;32(6):1145-56. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 Apr 26. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 24780153 Review.
References
-
- Deguine J.-P., Aubertot J.-N., Flor R. J., Lescourret F., Wyckhuys K. A. G., Ratnadass A.. Integrated Pest Management: Good Intentions, Hard Realities. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021;41(3):38. doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00689-w. - DOI
-
- European Union . Farm to Fork Strategy 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

