A high-efficiency palmprint recognition model integrating ROI and Gabor filtering
- PMID: 40455870
- PMCID: PMC12129327
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323373
A high-efficiency palmprint recognition model integrating ROI and Gabor filtering
Abstract
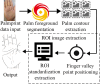
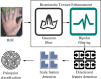
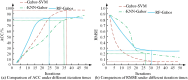
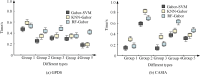
Palmprint recognition, as a biometric recognition technology, has unique individual recognition and high accuracy, and is broadly utilized in fields such as identity verification and security monitoring. Therefore, a palm print recognition model that integrates regions of interest and Gabor filters has been proposed to solve the problem of difficulty in feature extraction caused by factors such as noise, lighting changes, and acquisition angles that often affect palm print images during the acquisition process. This model extracts standardized feature regions of palmprint images through the region of interest method, enhances texture features through multi-scale Gabor filters, and finally uses support vector machines for classification. The experiment findings denote that the region of interest model performs better than other methods in terms of signal-to-noise ratio and root mean square error, with a signal-to-noise ratio of 0.89 on the GPDS dataset and 0.97 on the CASIA dataset. The proposed model performs the best in recognition accuracy and error convergence speed, with a final accuracy of 95%. The proposed model has the shortest running time, less than 0.4 seconds in all groups, especially less than 0.3 seconds in Group 4, demonstrating high recognition efficiency. The research conclusion shows that the palmprint recognition method combining regions of interest and Gabor filters has high efficiency and performance, and can effectively improve recognition accuracy.
Copyright: © 2025 Zhang, Xi. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Bimodal Biometric Verification Using the Fusion of Palmprint and Infrared Palm-Dorsum Vein Images.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Dec 12;15(12):31339-61. doi: 10.3390/s151229856. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26703596 Free PMC article.
-
Deformed Palmprint Matching Based on Stable Regions.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2015 Dec;24(12):4978-89. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2478386. Epub 2015 Sep 14. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2015. PMID: 26390453
-
Multi-Order Extension Codes for Palmprint Recognition.Int J Neural Syst. 2025 Aug;35(8):2550039. doi: 10.1142/S012906572550039X. Epub 2025 May 26. Int J Neural Syst. 2025. PMID: 40621645
-
Multifeature-based high-resolution palmprint recognition.IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2011 May;33(5):945-57. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.164. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2011. PMID: 20733215
-
An Improved Multispectral Palmprint Recognition System Using Autoencoder with Regularized Extreme Learning Machine.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2018 May 27;2018:8041609. doi: 10.1155/2018/8041609. eCollection 2018. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29977278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miao X, Xue C, Li X, Yang L. A real-time fatigue sensing and enhanced feedback system. Information. 2022;13(5):230. doi: 10.3390/info13050230 - DOI
-
- Min J, Cai M, Gou C, Xiong C, Yao X. Fusion of forehead EEG with machine vision for real-time fatigue detection in an automatic processing pipeline. Neural Comput Appl. 2022;35(12):8859–72. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07466-0 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

