Succinate drives gut inflammation by promoting FOXP3 degradation through a molecular switch
- PMID: 40457062
- PMCID: PMC12399925
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02166-y
Succinate drives gut inflammation by promoting FOXP3 degradation through a molecular switch
Abstract
Succinate levels are increased in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but its role in disease pathogenicity remains unknown. Here we showed that succinate promoted colitis in mice by reducing the expression of FOXP3 and increasing the expression of interleukin-17 in regulatory T (Treg) cells. Succinate selectively reduced the expression of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (OGDHc), the enzyme for succinyl-CoA synthesis, which in turn reduced FOXP3 succinylation and made FOXP3 lysine residues available for ubiquitination and FOXP3 protein degradation. Genetic deletion of Dlst, a member of OGDHc, in Treg cells led to reduced expression of FOXP3, impaired Treg cells function and severe gut inflammation. Restoring FOXP3 expression fully rescued the immune suppressive functions of Dlst-deficient Treg cells. In individuals with IBD, FOXP3 and OGDHc levels were reduced in Treg cells and negatively correlated with succinate levels and inflammation severity. This study identifies succinate as a pathogenic factor in IBD, uncovering a succinate-driven molecular switch that regulates FOXP3 stability and Treg cells function during inflammation.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
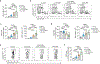

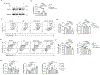
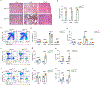



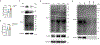








References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA257520/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- CA232347/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- T32 GM105538/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RO1DK124132/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- T32GM105538/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 DK135620/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA257520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA287701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM149439/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RO1DK135193/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 DK126908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK120330/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- T32GM149439/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- RO1DK135620/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 DK135193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK126908/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 DK124132/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA232347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120330/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

