Sequential bilateral retinal artery occlusions with promising visual prognosis in a diabetic patient: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 40457210
- PMCID: PMC12128277
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04166-w
Sequential bilateral retinal artery occlusions with promising visual prognosis in a diabetic patient: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Bilateral retinal artery occlusion (RAO) in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus is an extremely rare condition. Even with rigorous treatment, RAO often results in devastating visual impairment.
Case presentation: A 50-year-old female with Type 2 diabetes mellitus was referred to our hospital. Notably, she developed bilateral RAO sequentially within a mere five-month period. This rapid progression of the disease in both eyes is of particular interest.
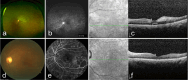
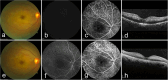
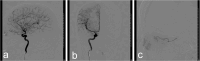
Observations: Fundus examination confirmed branch retinal artery occlusion (BRAO) in her left eye and central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) in her right eye. After timely intra-arterial thrombolysis, significant bilateral visual recovery was achieved. The patient's visual acuity in the left eye improved from 20/400 to 20/100 and in the right eye from 20/2000 to 20/33.3, indicating the effectiveness of this treatment approach in this case. Further examinations also showed positive results: the cherry-red spot in the macula disappeared, FFA indicated improved retinal artery perfusion, and OCT revealed a certain degree of restoration in the retinal structure.
Conclusion: This case highlights that metabolic disorders, like hyperlipidemia and diabetes, can be considered high-risk factors for the development of RAO. Prompt and effective intervention, such as timely intra-arterial thrombolysis, as demonstrated in this case, is crucial for preserving patients' visual prognosis.
Keywords: Bilateral retinal artery occlusion; Branch retinal artery occlusion; Central retinal artery occlusion; Intra-arterial thrombolysis; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was carried out following the institutional guidelines and ethical standards of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University (WDRY2022-K278). Consent for publication: Informed consent for publication was obtained from the patient. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

