Transcript profiling of plastid ferrochelatase two mutants reveals that chloroplast singlet oxygen signals lead to global changes in RNA profiles and are mediated by Plant U-Box 4
- PMID: 40457237
- PMCID: PMC12131553
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06703-7
Transcript profiling of plastid ferrochelatase two mutants reveals that chloroplast singlet oxygen signals lead to global changes in RNA profiles and are mediated by Plant U-Box 4
Abstract
Background: In response to environmental stresses, chloroplasts generate reactive oxygen species, including singlet oxygen (1O2), an excited state of oxygen that regulates chloroplast-to-nucleus (retrograde) signaling, chloroplast turnover, and programmed cell death (PCD). Yet, the central signaling mechanisms and downstream responses remain poorly understood. The Arabidopsis thaliana plastid ferrochelatase two (fc2) mutant conditionally accumulates 1O2, and Plant U-Box 4 (PUB4), a cytoplasmic E3 ubiquitin ligase, is involved in propagating 1O2 signals for chloroplast turnover and cellular degradation. Thus, the fc2 and fc2 pub4 mutants are useful genetic tools to elucidate these signaling pathways. Previous studies have focused on the role of 1O2 in promoting cellular degradation in fc2 mutants, but its impact on retrograde signaling from mature chloroplasts (the major site of 1O2 production) is poorly understood.
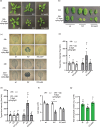
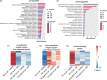
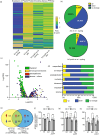
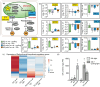
Results: To gain mechanistic insights into 1O2 signaling pathways, we compared transcriptomes of adult wt, fc2, and fc2 pub4 plants. The accumulation of 1O2 in fc2 plants broadly repressed genes involved in chloroplast function and photosynthesis, while inducing genes and transcription factors involved in abiotic and biotic stress, the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA), microautophagy, and senescence. Elevated JA and SA levels were observed in 1O2-stressed fc2 plants. pub4 reversed most of this 1O2-induced gene expression and reduced the JA content in fc2 plants. The pub4 mutation also blocked JA-induced senescence pathways in the dark. However, fc2 pub4 plants maintained constitutively elevated levels of SA even in the absence of bulk 1O2 accumulation.
Conclusions: Together, this work demonstrates that in fc2 plants, 1O2 leads to a robust retrograde signal that may protect cells by downregulating photosynthesis and ROS production while simultaneously mounting a stress response involving SA and JA. The induction of microautophagy and senescence pathways indicate that 1O2-induced cellular degradation is a genetic response to this stress, and the bulk of this transcriptional response is modulated by the PUB4 protein. However, the effect of pub4 on hormone synthesis and signaling is complex and indicates that an intricate interplay of SA and JA are involved in promoting stress responses and programmed cell death during photo-oxidative damage.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; Abiotic stress; Chloroplast; Jasmonic acid; Programmed cell death; Reactive oxygen species; Salicylic acid; Singlet oxygen.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Transcript profiling of plastid ferrochelatase two mutants reveals that chloroplast singlet oxygen signals lead to global changes in RNA profiles and are mediated by Plant U-Box 4.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 26:2024.05.13.593788. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.13.593788. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jun 3;25(1):747. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06703-7. PMID: 38798329 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Transcript profiling of plastid ferrochelatase two mutants reveals that chloroplast singlet oxygen signals lead to global changes in RNA profiles and are mediated by Plant U-Box 4.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 26:2024.05.13.593788. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.13.593788. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jun 3;25(1):747. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06703-7. PMID: 38798329 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The core autophagy machinery is not required for chloroplast singlet oxygen-mediated cell death in the Arabidopsis thaliana plastid ferrochelatase two mutant.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jul 19;21(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03119-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34281507 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic screen for dominant chloroplast reactive oxygen species signaling mutants reveals life stage-specific singlet oxygen signaling networks.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 10;14:1331346. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1331346. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38273946 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay of singlet oxygen and ABI4 in plant growth regulation.Trends Plant Sci. 2025 Feb;30(2):156-166. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2024.09.007. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Trends Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39414457 Review.
-
Singlet Oxygen in Plants: Generation, Detection, and Signaling Roles.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 3;21(9):3237. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093237. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32375245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Mg-Chelatase Subunit I Missense Mutant in Barley Exhibits a Cold-Sensitive Phenotype Under Field Conditions.Physiol Plant. 2025 Jul-Aug;177(4):e70434. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70434. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40762131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Triantaphylides C, Havaux M. Singlet oxygen in plants: production, detoxification and signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009;14(4):219–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

