Serum IL-40 is elevated in systemic sclerosis and is linked to disease activity, gastrointestinal involvement, immune regulation and fibrotic processes
- PMID: 40457473
- PMCID: PMC12128543
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03570-3
Serum IL-40 is elevated in systemic sclerosis and is linked to disease activity, gastrointestinal involvement, immune regulation and fibrotic processes
Abstract
Background: Interleukin 40 (IL-40) is a cytokine implicated in malignancies and rheumatic disorders. Its association with fibrotic mediators has been previously described. Since inflammation and fibrosis are hallmarks of systemic sclerosis (SSc), we aimed to analyze the role of IL-40 in SSc.
Methods: IL-40 levels were analyzed in the serum of 90 SSc patients and 75 healthy controls (HCs). IL-40 expression in dermal biopsies from 5 SSc patients and 5 HCs was assessed via immunohistochemistry. IL-40 was analyzed in 39 SSc patients with interstitial lung disease treated with cyclophosphamide (CPA) and in 24 SSc patients with active progressive disease treated with rituximab (RTX). SSc activity was assessed by the European Scleroderma Study Group (ESSG) index. The effect of recombinant IL-40 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 10 SSc patients was determined in vitro. IL-40 was analyzed in 24 individuals at risk of developing SSc (VEDOSS), who were categorized as progressors (n = 11) and nonprogressors (n = 13).
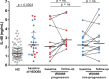
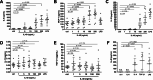
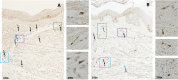
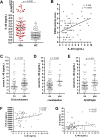
Results: IL-40 expression was elevated in the skin of SSc patients compared to HCs, particularly in fibroblasts and immune infiltrates. Serum IL-40 was increased in SSc compared to HCs (p < 0.0001) and was associated with ESSG (r = 0.372, p = 0.0005) and gastrointestinal involvement (p < 0.05). IL-40 correlated with serum IL-8 (r = 0.270, p = 0.019) and TGF-β1 (r = 0.301, p = 0.024) levels. In the CPA and RTX cohort, no significant changes in the serum IL-40 were observed upon treatment. Baseline and changes in IL-40 levels were associated with changes in several clinical parameters. IL-40 was elevated in patients at risk of SSc compared to HCs (p = 0.0003). No significant changes were observed in progressors vs. nonprogressors; however, IL-40 was associated with capillaroscopy findings (p < 0.05). IL-40 induced the upregulation of IL-6 (p = 0.002), MCP-1 (p = 0.002) and IL-10 (p = 0.002) in PBMCs from SSc patients in vitro.
Conclusions: IL-40 was upregulated in the skin and serum of SSc patients and was associated with disease activity, gastrointestinal involvement and fibrotic mediators. Our in vitro findings indicate that IL-40 might be involved in the immune response and fibrotic processes in SSc.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Interleukin 40; Systemic sclerosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee of the Institute of Rheumatology in Prague, Czech Republic. The reference number for ethics approval is 6485/2020. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- mith V, Scirè CA, Talarico R, Airo P, Alexander T, Allanore Y, Bruni C, Codullo V, Dalm V, De Vries-Bouwstra J, Della Rossa A, Distler O, Galetti I, Launay D, Lepri G, Mathian A, Mouthon L, Ruaro B, Sulli A, Tincani A, Vandecasteele E, Vanhaecke A, Vanthuyne M, Van den Hoogen F, Van Vollenhoven R, Voskuyl AE, Zanatta E, Bombardieri S, Burmester G, Eurico FJ, Frank C, Hachulla E, Houssiau F, Mueller-Ladner U, Schneider M, van Laar JM, Vieira A, Cutolo M, Mosca M, Matucci-Cerinic M. Systemic sclerosis: state of the Art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open. 2018;4(Suppl 1):e000782. 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000782. PMID: 30402270; PMCID: PMC6203100. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carnevale A, Silva M, Maietti E, Milanese G, Saracco M, Parisi S, Bravi E, De Gennaro F, Arrigoni E, Bodini FC, Fusaro E, Scirè CA, Sverzellati N, Ariani A. Longitudinal change during follow-up of systemic sclerosis: correlation between high-resolution computed tomography and pulmonary function tests. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40(1):213–219. 10.1007/s10067-020-05375-y. Epub 2020 Sep 3. PMID: 32880053. - PubMed
-
- Smith V, Pizzorni C, Riccieri V, Decuman S, Brusselle G, DE Pauw M, Deschepper E, Piette Y, Ruaro B, Sulli A, Vandecasteele E, Melsens K, DE Keyser F, Cutolo M. Stabilization of Microcirculation in Patients with Early Systemic Sclerosis with Diffuse Skin Involvement following Rituximab Treatment: An Open-label Study. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(5):995-6. 10.3899/jrheum.151018. PMID: 27134280. - PubMed
-
- Bellando-Randone S, Matucci-Cerinic M. Very early systemic sclerosis and pre-systemic sclerosis: definition, recognition, clinical relevance and future directions. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19:65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- GAUK114122/Grantová Agentura, Univerzita Karlova
- GAUK114122/Grantová Agentura, Univerzita Karlova
- GAUK114122/Grantová Agentura, Univerzita Karlova
- GAUK114122/Grantová Agentura, Univerzita Karlova
- NU21-05-00276, 023728/Ministerstvo Zdravotnictví Ceské Republiky
- NU21-05-00276, 023728/Ministerstvo Zdravotnictví Ceské Republiky
- NU21-05-00276, 023728/Ministerstvo Zdravotnictví Ceské Republiky
- NU21-05-00276, 023728/Ministerstvo Zdravotnictví Ceské Republiky
- NU21-05-00276, 023728/Ministerstvo Zdravotnictví Ceské Republiky
- SVV 260638/Ministerstvo Školství, Mládeže a Tělovýchovy
- SVV 260638/Ministerstvo Školství, Mládeže a Tělovýchovy
- LM2023033/Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Czech Republic
- LM2023033/Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Czech Republic
- LM2023033/Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Czech Republic
- LM2023033/Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Czech Republic
- LM2023033/Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Czech Republic
- LM2023033/Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure of Czech Republic
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

