EMA approved orphan medicines since the implementation of the orphan legislation
- PMID: 40457478
- PMCID: PMC12131831
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-025-03756-7
EMA approved orphan medicines since the implementation of the orphan legislation
Abstract
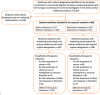
Background: In the European Union (EU), the orphan legislation, aiming to increase the number of pharmacotherapies available for rare diseases, came into force in April 2000. This study examined the development of the selection of orphan medicines granted marketing authorisation, their approved indications, and the number of orphan medicines developed for paediatric use in EU during 2000-2022. This study also examined the availability of the orphan medicines with a marketing authorisation in the Finnish market in order to demonstrate their country level uptake in a single member state.
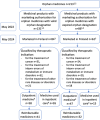
Methods: The material on orphan medicines' marketing authorisations and their introduction were collected from the European Commission's Community Registers in June 2022 and analysed with a qualitative document analysis. This study covered the period 2000-2022 since the introduction of the orphan legislation, and comparisons were made in 10-year periods of, 2001-2010 and 2011-2020.
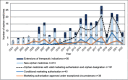
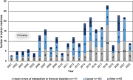
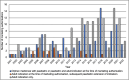
Results: By May 2022, there were 213 novel orphan medicines approved in Europe during the observation period. Of them, 67% (n = 142) were on the market in Finland in May 2024. The number of new orphan medicines approved in Europe doubled from 63 products in 2001-2010 to 127 products in 2011-2020. Several orphan medicines were developed for certain type of rare diseases, such as haematological cancers. The proportion of orphan medicines approved for paediatric use decreased from 55% in 2001-2010 to 42% in 2011-2020.
Conclusion: The number of orphan medicines available within EU increased significantly after the orphan legislation came into force. The development of orphan medicines seemed to often focus on diseases or disease groups that already have available treatment options, while several rare diseases remain without available treatment. Even though rare diseases are more common in children, orphan medicines have not been developed for paediatric use in the same proportion.
Keywords: Europe; Orphan medicine; Orphan medicines legislation; Rare disease; Selection of medicines.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: As the study is based on public documents from authorities, ethical review was not required. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orphan medicinal products in Europe and United States to cover needs of patients with rare diseases: an increased common effort is to be foreseen.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017 Apr 3;12(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0617-1. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017. PMID: 28372595 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the budget impact of orphan medicines in Europe: 2010 - 2020.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011 Sep 27;6:62. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-6-62. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011. PMID: 21951518 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan drugs, orphan diseases. The first decade of orphan drug legislation in the EU.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;69(4):1009-24. doi: 10.1007/s00228-012-1423-2. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23090701
-
[Hope for patients with rare diseases--"orphan" drugs].Cas Lek Cesk. 2006;145(4):296-300. Cas Lek Cesk. 2006. PMID: 16639930 Review. Slovak.
-
A regulatory overview about rare diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;686:193-207. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-9485-8_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20824447 Review.
References
-
- European Medicines Agency EMA. Procedural advice for orphan medicinal product designation. 2018. EMA/420706/2018. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/regulatory-procedural-guideline/p.... Accessed 22 January 2023
-
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 141/2000 of the European Parliament and of the Council on orphan medicinal products. http://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/eudralex/vol-1_en.
-
- European Medicines Agency EMA. Annual report on the use of the special contribution for orphan medicinal products. 2021. EMA/770190/2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/annual-report-use-special-.... Accessed 22 January 2023
-
- Bell SA, Smith T. A comparison of interventional clinical trials in rare versus non- rare diseases: an analysis of ClinicalTrials.gov. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:170. 10.1186/s13023-014-0170-0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency EMA. Rare diseases, orphan medicines. 2017. EMA/551338/2017. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/other/rare-diseases-orphan-medici.... Accessed 22 Jan 2023.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

