Inflammation Promotes Proteolytic Processing of the Prohormone Chromogranin A by Macrophages
- PMID: 40458085
- PMCID: PMC12127132
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf090
Inflammation Promotes Proteolytic Processing of the Prohormone Chromogranin A by Macrophages
Abstract
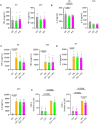
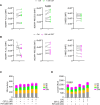
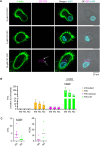
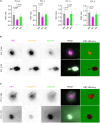
Chromogranin A (CgA), a 439-amino acid-long protein produced by neuroendocrine cells, is critical in health and disease. Through proteolytic processing, CgA is transformed into several bioactive peptides. These peptides, as well as CgA, have been implicated in various pathological conditions. Interestingly, CgA-derived peptides have opposing effects, such as catestatin (CST) and pancreastatin (PST), which have contrasting immunomodulatory properties. PST promotes a proinflammatory response, increasing the production of proinflammatory cytokines, whereas CST reduces proinflammatory and increases anti-inflammatory cytokines in mice. However, how CgA and CgA-derived peptides regulate the immune response is unknown, and most of our knowledge is based on mouse studies. Since multiple studies suggest that CgA and CgA-derived peptides influence macrophages, we aimed to investigate the interaction between CgA and human monocyte-derived macrophages. Therefore, we tested whether human macrophages produce CgA, are affected by CST and PST, and/or produce CST and PST. We found that human monocyte-derived macrophages and other immune cells do not produce CgA, and CST and PST have only minor effects on cytokine production and immune metabolism. However, proteases involved in the cleavage of CgA are differentially expressed in macrophages depending on their inflammatory phenotype, suggesting that CgA is increasingly converted into CST and PST in inflammatory conditions. As levels of CgA and its cleavage products CST and PST are associated with human diseases, it is essential to understand how they influence the immune response.
Keywords: chromogranin A; inflammation; macrophages; proteolytic processing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures


References
-
- Montero-Hadjadje M, Vaingankar S, Elias S, Tostivint H, Mahata SK, Anouar Y. Chromogranins A and B and secretogranin II: evolutionary and functional aspects. Acta Physiologica. 2008;192(2):309‐324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
