Triglyceride-glucose index and periodontitis: evidence from two population-based surveys
- PMID: 40458175
- PMCID: PMC12127200
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1558692
Triglyceride-glucose index and periodontitis: evidence from two population-based surveys
Abstract
Background: The relationship between the Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) index and periodontitis remains unclear. This study aims to elucidate this relationship using data from two large population-based surveys.
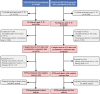
Methods: Datasets from NHANES (2009-2014) and KNHANES (2007-2018, except for 2011) were utilized. We applied multivariate logistic regression, stratified analysis, restricted cubic splines (RCS), and subgroup analyses to examine the correlation between the TyG index and periodontitis risk. The predictive value of the TyG index was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Mediation analyses investigated variables mediating this relationship.
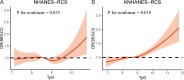
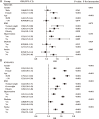
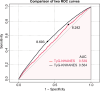
Results: The NHANES and KNHANES cohorts included 2,511 and 16,239 participants with periodontitis, respectively. After adjusting for covariates, the TyG index was significantly associated with periodontitis risk (NHANES: OR 1.19, 95%CI: 1.07-1.34; Q2 vs. Q1, OR 1.20, 95% CI: 1.02-1.42; Q4 vs. Q1, OR 1.23, 95%CI: 1.02-1.49. KNHANES: OR 1.09, 95% CI: 1.05-1.13; Q4 vs. Q1, OR 1.09, 95%CI: 1.02-1.17, P for trend = 0.025). RCS analyses revealed a nonlinear relationship. ROC curves indicated that the predictive values of the TyG index were 8.24 (NHANES) and 8.69 (KNHANES). Mediation analysis showed that inflammatory (alkaline phosphatase and white blood cell) and metabolic factors (vitamin D and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) partially mediated this association.
Conclusions: The observational analysis reveals a significant association between the TyG index and the risk of periodontitis. Further studies are needed to clarify the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: KNHANES; NHANES; insulin resistance; periodontitis; triglyceride-glucose index.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Long, Guo, Cui, Wei, Zhao, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of the triglyceride-glucose index and its related parameters with frailty.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 May 21;23(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02147-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38773587 Free PMC article.
-
The association between triglyceride-glucose index and its combination with systemic inflammation indicators and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general US population: NHANES 1999-2018.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 10;23(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02277-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39256829 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between different triglyceride glucose index-related obesity indices and periodontitis: results from NHANES 2009-2014.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 5;23(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02192-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38970059 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride glucose-waist to height ratio (TyG-WHtR) and hypertension in adults aged 18-60: a cross-sectional study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 May 26;25(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04853-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40419977 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the triglyceride-glucose index and liver fibrosis in adults with metabolism-related fatty liver disease in the United States: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017-2020.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 2;25(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03579-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39748306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Papapanou PN, Sanz M, Buduneli N, Dietrich T, Feres M, Fine DH, et al. . Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Clin Periodontol. (2018) 45 Suppl 20:S162–s170. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12946 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

