Tumor Lipid Signaling Involved in Hyperoxidative Stress Response: Insights for Therapeutic Advances
- PMID: 40458196
- PMCID: PMC12129048
- DOI: 10.33696/Signaling.6.132
Tumor Lipid Signaling Involved in Hyperoxidative Stress Response: Insights for Therapeutic Advances
Abstract
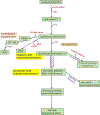
Most malignantly transformed cells are metabolically rewired to promote their survival and progression, even under conditions that would be unfavorable for normal counterparts. Arguably the most impactful metabolic transformation and recognized cancer hallmark is the reprogrammed lipid metabolism. Lipids are not only primary constituents of cell membranes but essential participants in fundamental cellular functions including cell signaling, protein regulation, energy provision, inflammation, and cell-cell interaction. Engagement of lipids in critical physiological functions in cells is additionally accentuated upon malignant transformation. Pivotal roles of lipids as influential inter- and intracellular signaling molecules, particularly under conditions of hyper oxidative stress, are delineated. Elaborated in more detail are SCAP/SREBP pathway and sphingolipid signaling cascades due to their roles of principal signaling networks determining tumor therapy responses. In the concluding section, an overview is provided of the process of lipid peroxidation and its impact in cancer cells sustaining oxidative stress with the outline of cell signaling functions of primary and secondary lipid peroxidation products. Much remains to be learned about the consequences of the fact that the lipid peroxidation process can extend beyond the site of initiation owing to (either spontaneous or transfer protein-mediated) translocation of peroxy radical species disseminating their impact to other subcellular sites.
Keywords: Hyper oxidative stress; Lipid metabolism rewiring; Lipid peroxidation; Lipid signaling; Metabolic reprograming.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Both authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
