Steroid hormone binding and modulation of Trichinella spiralis progesterone receptor: A computational approach
- PMID: 40458199
- PMCID: PMC12127865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102031
Steroid hormone binding and modulation of Trichinella spiralis progesterone receptor: A computational approach
Abstract
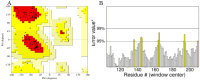
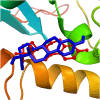
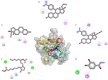
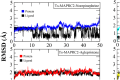
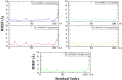
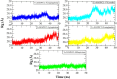
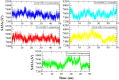
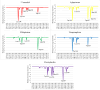
Trichinellosis, caused by Trichinella species, including Trichinella spiralis, is a foodborne zoonotic disease. Upon ingestion, ML swiftly invade the intra-multicellular niche of the small intestine, undergoing four rapid molts to mature into adults. In general, the route of transmission for T. spiralis nematodes occurs through ingestion of pork. Therefore, it is crucial to develop a vaccine that can deal with trichinellosis, particularly for humans and pigs. In this study, homology modelling, molecular docking, simulations and molecular mechanics-based scoring (MM/GBSA) are used to investigate the interaction between T. spiralis membrane-associated progesterone receptor component 2 (Ts-MAPRC2) and different steroids hormones. In the most favorable region, 93 amino acid residues (92.1 %) are located, while 7 amino acids (6.9 %) are located in the allowed region, showing that the model with a 93.33 ERRAT quality factor is good quality. The MD simulations were conducted for 50 ns to explore the affinities and stability of four hormones chosen from the docking studies that showed similar binding poses to the control hormone Mifepristone. Simulations showed that the selected hormones were potent Ts-MAPRC2 binders and can act as leads to determine their activity by biophysical assays. Discovery of these five steroid hormones and interactions with Ts-MAPRC2 could lead to new therapies and vaccines for trichinellosis.
Keywords: Molecular modeling; Simulation; Steroid hormones; Trichinella spiralis; Ts-MAPRC2.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Yang Y., Bai X., Li C., Tong M., Zhang P., Cai W., Liu X., Liu M. Molecular characterization of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from trichinella spiralis and its potential in inducing immune protection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019;9 doi: 10.3389/FCIMB.2019.00122/BIBTEX. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO . Multicriteria-based Ranking for Risk Management of Food-Borne Parasites: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Meeting, 3-7 September 2012, FAO Headquarters. WHO/Iris; Rome, Italy: 2014. https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/112672
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

