Application of Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Cutaneous Hemangioma and Vascular Malformation in a Cockscomb Model
- PMID: 40458204
- PMCID: PMC12127120
- DOI: 10.1155/drp/2012304
Application of Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Cutaneous Hemangioma and Vascular Malformation in a Cockscomb Model
Abstract
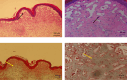
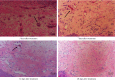
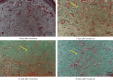
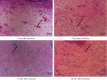
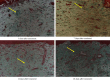
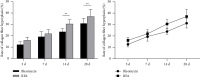
Background: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is an emerging technology for the effective treatment of cutaneous hemangioma and vascular malformation. However, there are few histopathological studies on the treatment of this disease with RFA. Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effect of RFA and associated histopathological changes in a cockscomb model of cutaneous hemangioma and vascular malformation. Methods: Thirty-two Leghorn chickens were randomly divided into two groups: RFA group (treated with RFA; 220 V, pulse rate: 15 ms) and control group (treated with 1 mg/mL bleomycin). At 3, 7, 14, and 28 days after treatment, histopathological changes in the cockscomb tissues were observed visually and microscopically using hematoxylin and eosin staining and Masson's trichrome staining. The rates of capillary reduction and collagen proliferation were examined. Results: The cockscomb in the RFA group developed scabs earlier than that in the bleomycin group, and the scabs were darker and more clearly defined. The RFA group showed a more severe inflammatory reaction than the bleomycin group. At 28 days, most scabs had fallen off in both groups, and the boundary was clearer in the RFA group. At 3, 7, and 14 days, the number of capillaries decreased in both groups, with a more obvious decrease in the RFA group. From Days 3 to 28, the number of capillaries in the RFA group showed a trend of gradual increase, whereas that in the bleomycin group showed a trend of gradual decrease, but there was no significant difference between the two groups at 28 days (p > 0.05). The collagenous fibers of cockscomb showed a trend of gradual increase in both groups. The collagenous fiber hyperplasia was higher in the RFA group than in the bleomycin group at 14 and 28 days (p < 0.01). Conclusion: RFA significantly reduced the capillary number and promoted tissue fibrosis. Compared with bleomycin, RFA showed a better effect and with no obvious side effects in treating a cockscomb model of cutaneous hemangioma and vascular malformation.
Keywords: bleomycin; hemangioma; radiofrequency ablation; vascular malformation.
Copyright © 2025 Hong-long Chen et al. Dermatology Research and Practice published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acute effect of a variable pulse width Nd:YAG laser combined with hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether-mediated photodynamic therapy on a cockscomb model of nevus flammeus.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020 Dec;29(12):1425-1431. doi: 10.17219/acem/126300. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 33389833
-
Percutaneous ultrasound-guided 'three-step' radiofrequency ablation for giant hepatic hemangioma (5-15 cm): a safe and effective new technique.Int J Hyperthermia. 2020;37(1):212-219. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2020.1732484. Int J Hyperthermia. 2020. PMID: 32106730
-
[Clinical study of radiofrequency ablation combined with lauromacrogol for the treatment of parotid gland hemangioma in infants].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Jul;32(4):254-8. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 30044565 Chinese.
-
Endovascular radiofrequency ablation for varicose veins: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011;11(1):1-93. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011. PMID: 23074413 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation in benign thyroid nodule treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2025 Feb;35(2):612-623. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10881-7. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39046500
References
-
- Liau J. Y., Lee J. C., Tsai J. H., Chen C. C., Chung Y. C., Wang Y. H. High Frequency of GNA14, GNAQ, and GNA11 Mutations in Cherry Hemangioma: a Histopathological and Molecular Study of 85 Cases Indicating GNA14 as the Most Commonly Mutated Gene in Vascular Neoplasms. Modern Pathology . 2019;32(11):1657–1665. doi: 10.1038/s41379-019-0284-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Horbach S. E., Lokhorst M. M., Saeed P., de Goüyon Matignon de Pontouraude C. M. F., Rothová A., van der Horst C. M. Sclerotherapy for Low-Flow Vascular Malformations of the Head and Neck: A Systematic Review of Sclerosing Agents. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery . 2016;69(3):295–304. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.10.045. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

