Spices and culinary herbs for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer: A comprehensive review with mechanistic insights
- PMID: 40458304
- PMCID: PMC12126743
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cpt.2024.07.003
Spices and culinary herbs for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer: A comprehensive review with mechanistic insights
Abstract
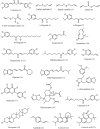
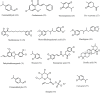
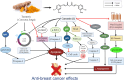
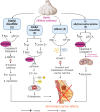
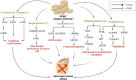
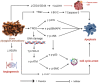
Breast cancer (BC) continues to be the primary malignant neoplasm affecting women. For many years, traditional approaches such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy, radiation, and surgical interventions have been employed to treat BC. However, these therapies often fall short due to considerable adverse effects and the development of multidrug resistance or tolerance. Spices and culinary herbs that have been utilized in culinary practices for millennia have also demonstrated therapeutic effects in traditional medicinal practices serving to both prevent and treat BC. This review aims to comprehensively explore the roles and underlying mechanisms through which spices and culinary herbs exert anti-BC properties. These natural ingredients exhibit diverse anti-BC effects that encompass diverse mechanisms, including the inhibition of BC cell proliferation, migration, metastasis, and angiogenesis, as well as the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. These actions are achieved by targeting signaling pathways such as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), notch signaling, Hedgehog signaling, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), and Wingless/int (Wnt)/β-catenin signaling pathways that are predominantly overexpressed in breast tumors or are exploited by them to promote cancer progression. Additionally, compounds such as curcumin, allicin, gingerol, zerumbone, diosgenin, capsaicin, piperine, quercetin, malabaricone C, eugenol, cardamomin, carnosol, cinnamaldehyde, sinigrin present in these spices and herbs may be more effective with reduced side effects against BC compared to conventional chemotherapeutic drugs. This review presents a concise overview of the potential contributions of spices, culinary herbs, and their potent bioactive constituents against BC, with particular emphasis on elucidating their mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Antineoplastic agents; Breast cancer; Complementary therapies; Phytochemicals; Spice.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethnomedicinal uses of Indian spices used for cancer treatment: A treatise on structure-activity relationship and signaling pathways.Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Oct 11;5:1845-1872. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.10.005. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36276240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-oncogenic perspectives of spices/herbs: A comprehensive review.EXCLI J. 2013 Dec 17;12:1043-65. eCollection 2013. EXCLI J. 2013. PMID: 27092039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Data-driven analysis of biomedical literature suggests broad-spectrum benefits of culinary herbs and spices.PLoS One. 2018 May 29;13(5):e0198030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198030. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29813110 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Review on Nutritional, Bioactive, and Medicinal Potential of Spices and Herbs and Their Application in Food Fortification and Nanotechnology.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Feb;195(2):1319-1513. doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-04132-y. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36219334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of therapeutic applicability and different signaling mechanism of various phytopharmacological agents for treatment of breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jul;139:111584. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111584. Epub 2021 May 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34243623 Review.
References
-
- Singla R.K., Wang X., Gundamaraju R., et al. Natural products derived from medicinal plants and microbes might act as a game-changer in breast cancer: a comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63:11880–11924. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2097196. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

