Chronic Analgesic Nephropathy with Atypical Squamous Metaplasia
- PMID: 40458341
- PMCID: PMC12128684
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.83400
Chronic Analgesic Nephropathy with Atypical Squamous Metaplasia
Abstract
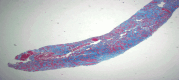
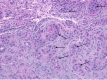
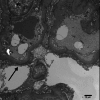
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a mainstay of pain management for various conditions. Their chronic use is associated with a well-documented risk of chronic analgesic nephropathy. Squamous metaplasia, a rare sequela of chronic analgesic nephropathy, involves the transformation of the normal epithelial lining of renal tubules into squamous epithelium. This metaplasia poses a diagnostic challenge, as it can mimic malignancy due to its atypical features. We present a case of a 64-year-old male patient with fibromyalgia and chronic NSAID use who developed chronic analgesic nephropathy concerning for squamous metaplasia, highlighting the potential for severe renal complications associated with chronic NSAID use. A kidney biopsy was evaluated using light microscopy, immunofluorescence microscopy, and electron microscopy. The kidney biopsy revealed histological features characteristic of chronic analgesic nephropathy, including severe interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. Additionally, extensive squamous metaplasia involving the renal tubules was identified at the glomerular level in the absence of a primary mass. This metaplasia exhibited worrisome features such as atypia and increased mitotic activity, signifying a heightened rate of cell division. This case report underscores the potential for chronic NSAID use to induce significant kidney damage, culminating in chronic analgesic nephropathy and squamous metaplasia with atypical characteristics. Integrating various microscopy techniques supports a definitive diagnosis and guides patient management.
Keywords: chronic analgesic nephropathy; kidney injury; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; oncology; squamous metaplasia.
Copyright © 2025, Mannion et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. West Virginia University Office of Human Research Protections issued approval (exempt). Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. (2024. What is kidney cancer? [ Oct; 2024 ]. 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/kidney-cancer/about/what-is-kidney-c... https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/kidney-cancer/about/what-is-kidney-c...
-
- Jha SK, Leslie SW, Aeddula NR. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls [Internet], StatPearls Publishing; [ Oct; 2024 ]. 2025. Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis. - PubMed
-
- Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) [ Oct; 2024 ]. 2023. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15456-kidney-infection-py... https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15456-kidney-infection-py...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
