Enhanced hemodynamic stability and patient satisfaction with ciprofol-remifentanil versus propofol-remifentanil for sedation in shorter-duration fiberoptic bronchoscopy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study
- PMID: 40458641
- PMCID: PMC12127319
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1498010
Enhanced hemodynamic stability and patient satisfaction with ciprofol-remifentanil versus propofol-remifentanil for sedation in shorter-duration fiberoptic bronchoscopy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of ciprofol-remifentanil versus propofol-remifentanil in patients undergoing fiberoptic bronchoscopy (FOB).
Methods: In this prospective, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial, 209 patients undergoing FOB were enrolled and equally divided into two groups (n = 106 each). The trial was registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR) under the registration number ChiCTR2400081603. Patients in the ciprofol-remifentanil group received ciprofol at a dose of 0.4 mg/kg, while those in the propofol-remifentanil group received propofol at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg. Both groups were pre-medicated with 1 μg/kg of remifentanil. Anesthesia was maintained with additional doses of the respective anesthetic agent as required to achieve a Modified Observer's Assessment of Alertness and Sedation (MOAA/S) scale score of ≤1. The primary outcome was the successful completion rate of FOB. Secondary outcomes included hemodynamic stability, incidence of adverse events such as hypoxemia and hypotension, patient and physician satisfaction, and the incidence of pain on injection.
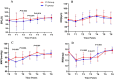
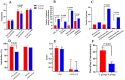
Results: The successful completion rate of FOB was 92.45% (98 of 106) in the ciprofol-remifentanil group and 90.57% (96 of 106) in the propofol-remifentanil group (p > 0.05). The ciprofol-remifentanil group demonstrated more stable hemodynamics, with significantly lower incidences of hypotension and hypoxemia compared to the propofol-remifentanil group (p < 0.05). Patient and physician satisfaction scores were significantly higher in the ciprofol-remifentanil group (p < 0.05). Additionally, the incidence of pain on injection was significantly lower in the ciprofol-remifentanil group (p < 0.01). Other adverse events, including coughing severity and intraoperative awareness, were similar between the two groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Ciprofol-remifentanil was non-inferior to propofol-remifentanil in terms of sedation during fiberoptic bronchoscopy;. Furthermore, ciprofol-remifentanil was associated with greater hemodynamic stability, reduced pain on injection, and higher satisfaction scores, suggesting that it may be a preferable alternative to propofol-remifentanil for FOB procedures.
Clinical trial registration: https://www.chictr.org.cn/, ChiCTR2400081603.
Keywords: ciprofol; fiberoptic bronchoscopy; hemodynamic; propofol; sedation.
Copyright © 2025 Nie, Zhang, Wang, Fang, Ma, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Du Rand IA, Barber PV, Goldring J, Lewis RA, Mandal S, Munavvar M, et al. British Thoracic Society interventional bronchoscopy guideline, British Thoracic Society guideline for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic flexible bronchoscopy in adults. Thorax. (2011) 66:iii1-21. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200713 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luo Z, Tu H, Zhang X, Wang X, Ouyang W, Wei X, et al. Efficacy and safety of HSK3486 for anesthesia/sedation in patients undergoing Fiberoptic bronchoscopy: a multicenter, double-blind, Propofol-controlled, randomized, phase 3 study. CNS Drugs. (2022) 36:301–13. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00890-1, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

