Engineering of antimicrobial peptide Brevinin-1pl: arginine, lysine, and histidine substitutions enhance antimicrobial-anticancer efficacy with reduced cytotoxicity
- PMID: 40458657
- PMCID: PMC12127288
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1579097
Engineering of antimicrobial peptide Brevinin-1pl: arginine, lysine, and histidine substitutions enhance antimicrobial-anticancer efficacy with reduced cytotoxicity
Abstract
Introduction: Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are promising candidates for combating multidrug-resistant infections, but their clinical application is often limited by challenges such as poor selectivity and high cytotoxicity. This study aimed to optimize the therapeutic potential of brevinin-1pl, a frog-derived AMP with broad-spectrum antimicrobial and anticancer activities.
Methods: Major experimental approaches encompassed antibacterial activity evaluation, hemolytic potential assessment, bactericidal rate determination via time-kill kinetics, SYTOX Green-based membrane integrity analysis, and MTT assays for anti-proliferative effects.
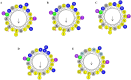
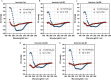
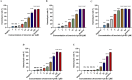
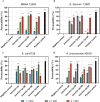
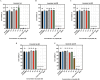
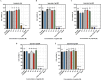
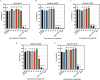
Results: Substitutions with arginine (brevinin-1pl-2R and brevinin-1pl-5R) enhanced activity against Gram-positive bacteria but reduced efficacy against Gram-negative strains. Lysine substitution (brevinin-1pl-6K) decreased activity against Gram-positive bacteria due to reduced hydrophobicity. In contrast, histidine substitution (brevinin-1pl-3H) showed diminished activity against Gram-negative bacteria (e.g., MRSA MIC increased from 2 µM to 4 µM) but reduced hemolysis, indicating improved selectivity. Mechanistic studies using SYTOX green assays confirmed membrane disruption as a primary mode of action, while suggesting alternative mechanisms for Gram-positive Enterococcus faecium and Gram-negative Escherichia coli. The brevinin-1pl and its analogues demonstrated significant inhibitory efficacy against both MCF-7 breast cancer cells and H838 non-small cell lung cancer cells at a concentration of 10-4 M. Notably, brevinin-1pl-3H exhibited low cytotoxicity toward normal HaCaT cells despite its high hydrophobicity, suggesting potential for dermatological applications.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that strategic amino acid substitutions can optimize the therapeutic potential of AMPs, offering a promising approach to develop peptides with enhanced efficacy and reduced clinical side effects.
Keywords: amino acid substitutions; anticancer activity; antimicrobial peptide; brevinin-1; drug-resistant; selectivity and cytotoxicity.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zeng, Chen, Wang, Wang, Zhou, Jiang, Chen, Fang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham P., Sundaram A., R A., V R., George S., Kumar K. S. (2015). Structure-activity relationship and mode of action of a frog secreted antibacterial peptide B1CTcu5 using synthetically and modularly modified or deleted (SMMD) peptides. PloS One 10 (5), e0124210. 10.1371/journal.pone.0124210 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators Ikuta Ikuta, K. S., Sharara F., Swetschinski L., Robles Aguilar G., Gray A., et al. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet London, Engl. 399 (10325), 629–655. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

