Mixtures of PRR Ligands Partly Mimic the Immunomodulatory Response of γ i Staphylococcus aureus, Enhancing Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
- PMID: 40458752
- PMCID: PMC12127128
- DOI: 10.1155/sci/1445520
Mixtures of PRR Ligands Partly Mimic the Immunomodulatory Response of γ i Staphylococcus aureus, Enhancing Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
Abstract
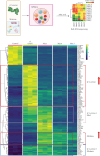
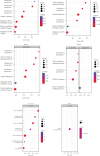
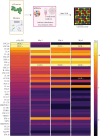
Recent evidence indicates the potential of gamma-irradiated (γi) Staphylococcus aureus to be used as an osteo-immunomodulator for bone regeneration. This study aims at characterizing the inflammatory milieu caused by the stimulation of γi S. aureus in immune cells and investigates its effects on MSC osteogenic differentiation. Furthermore, we aimed to recreate the immune-modulatory response exhibited by γi S. aureus by using a mixture of various synthetic pathogen recognition receptor (PRR) ligands consisting of TLR2, TLR8, TLR9, and NOD2 agonists. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMCs), isolated from healthy human donors, were exposed to γi S. aureus or seven different ligand mixtures. After 24 h, the conditioned medium (CM) from the hPBMCs was collected and its effects on hMSC osteogenic differentiation were investigated by assessing alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and matrix mineralization. The hPBMCs and their CM were also analyzed by bulk RNA sequencing and for cytokine secretion. CM from the γi S. aureus and the mixture consisting of Pam3CSK4, C-class CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN C), and murabutide targeting TLR2, TLR9, and NOD2 showed a fivefold increase in ALP and matrix mineralization in a donor-dependent manner. These effects were due to the upregulation of inflammatory signaling pathways, which led to an increase in cytokines and chemokines TNF, interleukin (IL)-6, IFN-γ, IL-1α, CXCL10, CCL18, CCL17, CXCL1, and CCL5. Upregulation of genes like BMP2R, BMP6R, BGLAP, and others contributed to the upregulation of osteogenic pathways in the hPBMCs stimulated with γi S. aureus and the aforementioned mix. Thus, formulations with mixtures of PRR ligands may serve as immune-modulatory osteogenesis-enhancing agents.
Keywords: PRR ligands; Staphylococcus aureus; bone regeneration; immune modulation; inflammation; pathogen recognition molecular patterns.
Copyright © 2025 Paree Khokhani et al. Stem Cells International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

