Xiaoyao San ameliorates maternal inflammation-induced neurobehavioral deficits by modulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis in offspring
- PMID: 40458794
- PMCID: PMC12127538
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1563496
Xiaoyao San ameliorates maternal inflammation-induced neurobehavioral deficits by modulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis in offspring
Abstract
Background: XiaoYao San (XYS), a classical Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), has demonstrated efficacy in alleviating stress-related neuropsychiatric disorders. However, its therapeutic potential against maternal immune activation (MIA)-induced neurobehavioral impairments remains unexplored. This study aims to investigate the neuroprotective effects of XYS on MIA-related behavioral dysfunctions and elucidate its underlying mechanisms.
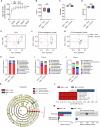
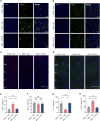
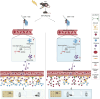
Results: Using a poly (I:C)-induced MIA mouse model, we demonstrated that XYS effectively ameliorates autism spectrum disorder (ASD) related behavioral phenotypes. Mechanistic investigations revealed that XYS exerts its therapeutic effects through: (1) Attenuation of core behavioral deficits including enhanced social interaction and reduced repetitive behaviors; (2) Downregulation of intestinal amino acid transporters; (3) Restoration of cerebral glutamate-GABA balance via modulation of glutamine pathway; (4) Structural remodeling of gut microbiota with specific enrichment of Bacteroides spp. Notably, B. uniformis was identified as a key microbial mediator capable of recapitulating XYS-mediated neurophysiological improvements through metabolic regulation.
Conclusion: This study elucidates XYS as a multi-target therapeutic agent that coordinately modulates gut microbial ecosystems, amino acid homeostasis, and neurotransmitter homeostasis. The findings provide novel insights into the gut-brain axis mechanisms of TCM formulations, offering a scientific foundation for developing microbiota-based intervention strategies for neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: Xiaoyao san; amino acid transporter; gut microbiota; maternal immune activation (MIA); neurodevelopmental disorders.
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Zhu, Zhang, Shi, Zhong, Xia, Ding and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Andersen J. V., Christensen S. K., Westi E. W., Diaz-delCastillo M., Tanila H., Schousboe A., et al. (2021a). Deficient astrocyte metabolism impairs glutamine synthesis and neurotransmitter homeostasis in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 148, 105198. 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105198 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

