Modulating the gut microbiota and inflammation is involved in the effect of diosgenin against diabetic nephropathy in rat
- PMID: 40458807
- PMCID: PMC12127415
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1555849
Modulating the gut microbiota and inflammation is involved in the effect of diosgenin against diabetic nephropathy in rat
Abstract
Background: Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a severe complication of diabetes, which has been increasingly associated with gut microbiota dysbiosis and inflammatory dysregulation.
Objective: This study investigates the dual therapeutic potential of diosgenin (DIO), a steroidal sapogenin, in modulating the gut-kidney axis and NLRP3 inflammasome activity in a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced DN rat model.
Methods: Oral DIO administration (20 mg/kg, 8 weeks) was used to treat the DN rats. The study assessed the effects on metabolic and renal function parameters, renal apoptosis and fibrosis, gut microbiota diversity, and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the kidney.
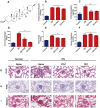
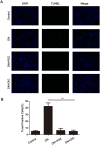
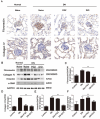
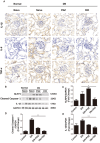
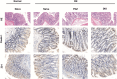
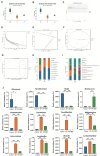
Results: DIO treatment ameliorated the progression of DN, improving metabolic and renal function. It attenuated renal apoptosis and fibrosis and restored gut microbiota diversity, particularly enriching the abundance of Lachnospiraceae and Eubacterium. Mechanistically, DIO suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the kidney, disrupted the LPS-TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascade, and reduced systemic pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6).
Conclusion: DIO is a multitarget agent that addresses both gut microbiota homeostasis and NLRP3-driven inflammation, presenting a novel therapeutic strategy for DN through modulation of the gut-kidney axis.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; anti-inflammatory; diabetic nephropathy; diosgenin; gut microbiota.
Copyright © 2025 Shanshan, Shu, Xiao, Kuerban, Hao, Yujie, Rong, Yuhuan and Yongfang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bian X., Snow Z. K., Zinn C. J., Gowan C. C., Conley S. M., Bratulin A. L., et al. (2025). Activin A antagonism with follistatin reduces kidney fibrosis, injury, and cellular senescence-associated inflammation in murine diabetic kidney disease. Kidney360. 10.34067/KID.0000000776 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

