Interplay Between Cortical and Neurocardiac Interoceptive Processes and its Association with Self-Reported Interoceptive Sensibility
- PMID: 40459802
- PMCID: PMC12134038
- DOI: 10.1007/s10548-025-01122-1
Interplay Between Cortical and Neurocardiac Interoceptive Processes and its Association with Self-Reported Interoceptive Sensibility
Abstract
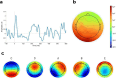
Interoception, the process of sensing and interpreting internal bodily signals, plays a crucial role in emotional regulation, decision-making, and overall well-being. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between self-reported interoceptive processes, assessed through the Body Perception Questionnaire (BPQ), and psychophysiological measures of interoception, including cardiac autonomic markers (HF-HRV and RMSSD), cortical processing of cardiac signals (heartbeat-evoked potentials, HEPs), and EEG microstates. We recorded EEG and ECG from 64 healthy volunteers during open-eyed resting state. A positive association was found between the Subdiaphragmatic Reactivity subscale of the BPQ and the coverage of microstate A, a spatial configuration linked to the activation of temporal brain regions, arousal, and sensory processing. No associations were observed between BPQ scores and cardiac measures or HEP amplitudes, suggesting that subjective reports may not align with psychophysiological indices of interoception. Associations were found between HEP amplitudes and microstates A and B, as well as between HRV measures and microstate D, highlighting potential links between autonomic functioning and brain activity during resting state. Although the BPQ is a widely used tool to assess interoceptive sensibility, it may not fully capture the complexity of this construct. These findings provide insight into the complex interplay between self-reported interoception and psychophysiological markers, while emphasizing the need for further research to clarify these relationships and their implications for emotional and cognitive processing.
Keywords: Heart-Brain Axis; Heartbeat Evoked Potentials; Interoception; Microstates.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

