Hydration Contribution to the Solvation Free Energy of Water-Soluble Polymers
- PMID: 40459969
- PMCID: PMC12235621
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5c01009
Hydration Contribution to the Solvation Free Energy of Water-Soluble Polymers
Abstract
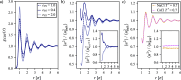
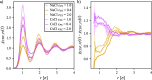
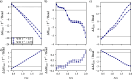
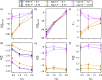
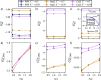
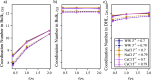
We study the solvation free energy of model water-soluble polymers with an emphasis on better understanding the entropic contribution deriving from the formation of a dynamic hydration layer (DHL). To isolate the solvation free energy due to polymer hydration from contributions that arise from changes in the polymer conformation (and thus solvent-accessible surface area) that ordinarily accompany solvation, we restrict a polymer chain in a rod-like configuration. As in recent works, the nanoscale mobility gradient around the polymer chain, defining the DHL, is quantified through the determination of the Debye-Waller parameter, ⟨u2⟩, for solvent in the vicinity of the polymer. This gradient enables us to easily visualize the DHL around the polymer. Direct computation of the free energy of solvation indicates a large entropic contribution that correlates with changes in Kirkwood-Buff integrals, which allow us to quantify specific ion effects on polymer solvation. While the water mobility exhibits a significant dependence on the strength of the polymer-solvent interaction in the nanoscale DHL, we unexpectedly found no additional specific ion effect on the mobility within the DHL relative to the bulk solution and, moreover, we find no change in the spatial extent of the DHL to within experimental uncertainty. On the other hand, we find an excess density of CsCl close to the polymer and density depletion of NaCl, consistent with previous suggestions that chaotropic ions partition toward polymer interfaces. Our work indicates that polymer hydration can make a large contribution to polymer solvation free energy, and we expect this phenomenon to be important in relation to understanding the thermodynamics of molecular self-assembly and phase separation processes of water-soluble polymers.
Figures
References
-
- Bayliss N., Schmidt B. V. K. J.. Hydrophilic Polymers: Current Trends and Visions for the Future. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2023;147:101753. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2023.101753. - DOI
-
- Kazemi Shariat Panahi H., Dehhaghi M., Amiri H., Guillemin G. J., Gupta V. K., Rajaei A., Yang Y., Peng W., Pan J., Aghbashlo M.. et al. Current and Emerging Applications of Saccharide-Modified Chitosan: A Critical Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023;66:108172. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108172. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pinho De Aguiar K. L. N., Palermo L. C. M., Mansur C. R. E.. Polymer Viscosifier Systems with Potential Application for Enhanced Oil Recovery: A Review. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. – Rev. D’IFP Energy Nouv. 2021;76:65. doi: 10.2516/ogst/2021044. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

