Robotic versus Electromagnetic Bronchoscopy for Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions: A Randomized Trial (RELIANT)
- PMID: 40460390
- PMCID: PMC12432399
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202409-1846OC
Robotic versus Electromagnetic Bronchoscopy for Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions: A Randomized Trial (RELIANT)
Abstract
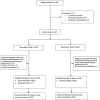
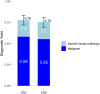
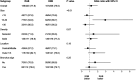
Rationale: Robotic-assisted bronchoscopy has emerged as an alternative to electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy for patients undergoing bronchoscopic biopsy of a peripheral pulmonary lesion. Although both platforms are routinely used in clinical practice, comparative effectiveness data are lacking. Objectives: We sought to compare the effectiveness of robotic-assisted and electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy for the evaluation of peripheral pulmonary lesions. Methods: In an investigator-initiated, single-center, cluster-randomized noninferiority trial, we assigned patients undergoing diagnostic bronchoscopy for evaluation of a peripheral pulmonary lesion to either robotic-assisted or electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy. The cluster randomization unit was the operating room in which patients were scheduled. The primary outcome was the diagnostic yield of the procedure, defined as the proportion of cases yielding lesional tissue. Secondary and safety outcomes included procedure duration and complications. Measurements and Main Results: Among the 411 patients included in the modified intention-to-treat analysis, lesional tissue was obtained in 158 of 203 (77.8%) patients in the robotic-assisted group and 157 of 208 (75.5%) patients in the electromagnetic group; the P value for noninferiority was 0.007. The median duration of bronchoscopy was 37 minutes in the robotic-assisted group and 32 minutes in the electromagnetic group (difference, 5 min; 95% confidence interval = 2.0-7.7). Pneumothorax occurred in 4 patients in the robotic-assisted group and 6 patients in the electromagnetic group. Conclusions: In patients undergoing bronchoscopy for the evaluation of a peripheral pulmonary lesion, the diagnostic yield of robotic-assisted bronchoscopy was not inferior to that of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT05705544).
Keywords: bronchoscopy; diagnostic yield; electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy; peripheral lung lesions; robotic-assisted bronchoscopy.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diagnostic Bronchoscopy for Peripheral Lung Lesions: When Innovation Races to Meet Demand.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2025 Sep;211(9):1541-1542. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202506-1374ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40824178 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gould MK, Tang T, Liu IL, Lee J, Zheng C, Danforth KN, et al. Recent trends in the identification of incidental pulmonary nodules. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2015;192:1208–1214. - PubMed
-
- Criner GJ, Eberhardt R, Fernandez-Bussy S, Gompelmann D, Maldonado F, Patel N, et al. Interventional bronchoscopy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2020;202:29–50. - PubMed
-
- Katsis J, Roller L, Aboudara M, Pannu J, Chen H, Johnson J, et al. Diagnostic yield of digital tomosynthesis-assisted navigational bronchoscopy for indeterminate lung nodules. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol . 2021;28:255–261. - PubMed
-
- Low SW, Lentz RJ, Chen H, Katsis J, Aboudara MC, Whatley S, et al. Shape-sensing robotic-assisted bronchoscopy vs digital tomosynthesis-corrected electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy: a comparative cohort study of diagnostic performance. Chest . 2023;163:977–984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

