Non-Linear Relationship Between Alcohol Consumption and Neurological Outcomes in Patients With Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Presenting to the Emergency Department
- PMID: 40461141
- PMCID: PMC12133598
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e96
Non-Linear Relationship Between Alcohol Consumption and Neurological Outcomes in Patients With Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Presenting to the Emergency Department
Abstract
Background: Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) is a major public health issue associated with low survival rates and poor neurological outcomes. Comorbidities and various triggers are associated with OHCA incidence and outcomes. However, the association between alcohol consumption and the neurological prognosis in patients with OHCA remains unknown. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the potential association between the frequency of alcohol consumption and neurological outcomes in patients with OHCA.
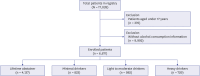
Methods: This retrospective observational study used data from the Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium registry, encompassing 62 hospitals in Korea. Patients aged > 18 years who experienced OHCA and were transported by the public emergency medical service system were included. Alcohol consumption was categorized into four groups: never drinkers, light drinkers, moderate drinkers, and heavy drinkers. The primary outcome measured was a favorable neurological outcome at hospital discharge (cerebral performance category score 1 or 2).
Results: Among the 6,671 enrolled patients, 14.7% had favorable neurological outcomes. The odd ratio of achieving a good neurologic outcome was reduced by 0.597 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.444-0.802; P < 0.001), 0.650 (95% CI, 0.431-0.983; P = 0.041), and 0.666-fold (95% CI, 0.448-0.989; P = 0.044) for never, light, and heavy drinkers, respectively, compared to moderate drinkers.
Conclusion: This study revealed a nonlinear association between the frequency of alcohol consumption and neurological prognosis in patients with OHCA. Therefore, future studies should focus on investigating the mechanism underlying the potential brain-protective effects of alcohol to further understand its impact on neurological recovery following OHCA.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03222999.
Keywords: Alcohol Consumption; Korea; Neurological Outcome; Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest.
© 2025 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
-
- Berdowski J, Berg RA, Tijssen JG, Koster RW. Global incidences of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and survival rates: systematic review of 67 prospective studies. Resuscitation. 2010;81(11):1479–1487. - PubMed
-
- Pak JE, Kim KH, Shin SD, Song KJ, Hong KJ, Ro YS, et al. Association between chronic liver disease and clinical outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2021;158:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical