Regional cerebral oxygen saturation references in extremely and very preterm neonates using neonatal sensors: a prospective observational cohort study
- PMID: 40461271
- PMCID: PMC12142085
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjpo-2024-003239
Regional cerebral oxygen saturation references in extremely and very preterm neonates using neonatal sensors: a prospective observational cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Reference values of regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rScO2) in preterm neonates across gestational age (GA) groups remain undefined. This study aimed to establish rScO2 references for neonates born before 32 weeks of gestation.
Design: A prospective observational cohort study.
Setting: Large tertiary neonatal referral centre in Croatia.
Patients: Preterm neonates without major comorbidities born between 2018 and 2022 with normal cranial ultrasound findings.
Interventions: rScO2 was assessed with near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) using neonatal sensors.
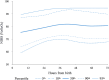
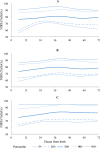
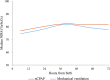
Main outcome measures: The primary analysis provided rScO2 reference ranges for the entire preterm neonatal cohort, followed by stratified analyses based on GA: extremely preterm, <28.0 weeks; very preterm, 28.0-30.0 weeks; and very preterm, 30.1-32.0 weeks. Quantile regression was used to estimate the selected rScO2 percentiles (5th, 10th, 50th, 90th and 95th) from 6 to 72 hours after birth.
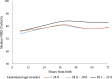
Results: 114 neonates with median (IQR) GA of 29.9 (29.1-31.5) weeks were included: 22% were EP<28w, 29% were VP28-30w and 49% were VP>30-32w. The median rScO2 was 75.6% at 6 hours, 79.5% over the first 24 hours and exceeding 80% in the subsequent 48 hours. When analysed separately, notable differences emerged across prematurity categories, with the highest median rScO2 observed in the VP>30-32w group. Supplementary analyses, comparing rScO2 values across the three GA groups, revealed significant differences at 48 and 72 hours. The majority of the estimated rScO2 fifth percentiles between 6 and 72 hours were in the range ≥60%, with a single lowest estimate of 56.3% at 6 hours in the EP<28w group. Thus, for all subgroups, the estimated fifth percentile of rScO2 was above the brain hypoxic threshold.
Conclusions: The use of age-appropriate neonatal NIRS sensors provided the rScO2 reference values for very and extremely preterm neonates without major comorbidities 6-72 hours after birth.
Keywords: Neonatology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Shoji H, Sato N, Ozaki H. P8-14 Evaluation of olfactory sensation in people with profound and/or multiple disabilities revealed by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;121:S150. doi: 10.1016/S1388-2457(10)60617-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
