Efficient generation of germline chimeras in a non-rodent species using rabbit induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 40461482
- PMCID: PMC12134177
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60314-2
Efficient generation of germline chimeras in a non-rodent species using rabbit induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
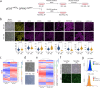
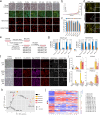
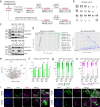
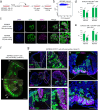
Pluripotent stem cells have long been used to produce knockout mice via germline chimera technology. However, aside from the rat, this approach has not been successfully applied to other mammals. Here, we demonstrate that rabbit induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) can be reprogrammed using KLF2, ERAS and PRMT6, enabling them to efficiently colonize embryos. These chimeric embryos can develop into fetuses and newborn rabbits, with iPSCs contributing up to 100 % to certain organs. Notably, female rabbits generated through this method are healthy and transmit the iPSC genome to their offspring with a high efficiency, demonstrating germline chimerism. This advancement establishes a foundation for developing rabbit models of human disease with complex genetic traits.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


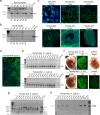
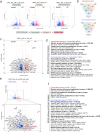
References
-
- Bradley, A., Evans, M., Kaufman, M. H. & Robertson, E. Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature309, 255–256 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Okita, K., Ichisaka, T. & Yamanaka, S. Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature448, 313–319 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Nichols, J. & Smith, A. Naive and primed pluripotent states. Cell Stem Cell4, 487–492 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Brons, I. G. et al. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature448, 191–195 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Tesar, P. J. et al. New cell lines from mouse epiblast share defining features with human embryonic stem cells. Nature448, 196–199 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ANR-18-CE13_023/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-10-LABX-73/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-10-LABX-0061/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-11-LABX-0042/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-11-IDEX-0007/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-11-INBS-0003/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- ANR-21-CE20-0018-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- DEQ20170336757/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (Foundation for Medical Research in France)
- EQU202303016295/Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (Foundation for Medical Research in France)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

