Epigenetic regulation of neural stem cell aging in the mouse hippocampus by Setd8 downregulation
- PMID: 40461639
- PMCID: PMC12218407
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00455-8
Epigenetic regulation of neural stem cell aging in the mouse hippocampus by Setd8 downregulation
Abstract
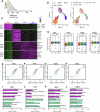
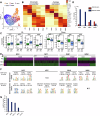
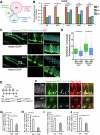
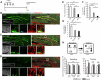
Neural stem cells (NSCs) in the mammalian brain decline rapidly with age, leading to impairment of hippocampal memory function in later life. However, the relationship between epigenetic remodeling and transcriptional regulation that compromises hippocampal NSC activity during the early stage of chronological aging remains unclear. Here, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and single-cell ATAC sequencing (scATAC-seq) on NSCs and newly generated neurons across different stages. Integrated data analysis revealed continuous alterations in the chromatin profile of hippocampal NSCs and their progeny from neonatal to mature adult stages, accompanied by consistent changes in transcriptional profiles. Further, decreased expression of Setd8, encoding the enzyme for histone H4 monomethylation at lysine 20 (H4K20me1), underlies age-related changes in mouse hippocampal NSCs. Notably, depletion of Setd8 elicits alterations in gene expression and epigenetic regulation that phenocopy age-related changes, and impairs NSC activity, leading to hippocampal memory deficits. Together, our study provides a global map of longitudinal chromatin and transcriptome changes during brain aging and identifies mechanistic insights into early-onset decline of NSC activity and hippocampal neurogenesis that precedes functional aging.
Keywords: Aging; Epigenetics; Hippocampus; Neural Stem Cell.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcription Factor EB Overexpression through Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Promoter Disrupts Neuronal Lamination by Dysregulating Neurogenesis during Embryonic Development.Dev Neurosci. 2025;47(1):40-54. doi: 10.1159/000538656. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Dev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 38583418 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Analysis of Single-Cell Transcriptomic Datasets Reveals Conserved Neurogenic Gene Signatures and New Insights Into Neural Stem Cell Aging.Aging Cell. 2025 Aug;24(8):e70106. doi: 10.1111/acel.70106. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 40464165 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrodin attenuates high fructose-induced sweet taste preference decrease by inhibiting hippocampal neural stem cell ferroptosis.J Adv Res. 2025 Aug;74:429-442. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.09.025. Epub 2024 Sep 29. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39353531 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease: Multimodal Therapeutics and the Neurogenic Impairment Index Framework.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 25;26(13):6105. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136105. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult human neurogenesis: early studies clarify recent controversies and go further.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Jan;37(1):153-172. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00864-8. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 34739659
References
-
- Artegiani B, Lyubimova A, Muraro M, van Es JH, van Oudenaarden A, Clevers H (2017) A single-cell RNA sequencing study reveals cellular and molecular dynamics of the hippocampal neurogenic niche. Cell Rep 21:3271–3284 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP16H06527/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP21H02808/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP18K14820/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP23K18451/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20J20975/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

