Chromosome-level genome assembly and anticoagulant protein annotation of the buffalo leech Hirudinaria bpling (Hirudinea: Hirudinidae)
- PMID: 40461966
- PMCID: PMC12131632
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11690-y
Chromosome-level genome assembly and anticoagulant protein annotation of the buffalo leech Hirudinaria bpling (Hirudinea: Hirudinidae)
Abstract
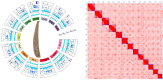
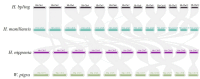
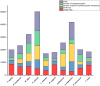
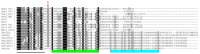
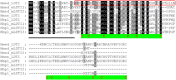
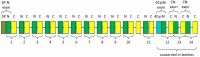
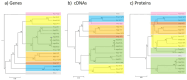
This study aimed to obtain and analyze the chromosome-level genome assembly of Hirudinaria bpling, a species vital for aquatic ecosystem health and medical research. Understanding its genomic information is crucial for advancing its medical applications and elucidating its ecological role. We assembled the genome of H. bpling using a combination of PacBio HiFi long reads, Illumina sequencing, and Hi-C chromosome conformation capture techniques. This approach allowed us to achieve a high-resolution genome assembly with detailed chromosomal organization. The final genome assembly of H. bpling is 144.08 Mb, with an N50 size of 11.27 Mb, anchored onto thirteen pseudo-chromosomes. BUSCO analysis indicated a genome completeness of 96.20%. We annotated a total of 20,126 protein-coding genes and identified 18.80% repetitive elements within the genome. Phylogenetic analysis included nine other leech species, positioning H. bpling as a sister taxon to Hirudo manillensis. A comparative analysis focused on the identification of putative anticoagulant proteins (e.g. Hirudin, Antistasin, Hirustasin, Therostasin, Bdellastasin, Guamerin/Piguamerin, Gelin, Bplins, Saratin, Eglin C, Bdellin B-3, LDTI, Hyaluronidase, Destabilase, Apyrase, Leech carboxypeptidase inhibitor, Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, Lefaxin, Progranulin), identifying conserved regions and evolutionary relationships among these proteins across different leech species. As a medically significant species, H. bpling offers promising opportunities for research into anticoagulant therapies. This study provides a comprehensive genomic and phylogenetic analysis of H. bpling, offering new insights into leech genomics and the evolution of anticoagulant genes. The findings enhance our understanding of the genetic and evolutionary mechanisms underlying anticoagulant production in leeches.
Keywords: Hirudinaria bpling; Anticoagulant proteins; Genomic sequencing; Phylogenetic analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Draft Genome of the Asian Buffalo Leech Hirudinaria manillensis.Front Genet. 2020 Jan 16;10:1321. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01321. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32010187 Free PMC article.
-
Biodiversity of the Buffalo Leeches Genus Hirudinaria (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) in Southern Thailand Revealed from DNA Barcoding.Zool Stud. 2022 Dec 26;61:e84. doi: 10.6620/ZS.2022.61-84. eCollection 2022. Zool Stud. 2022. PMID: 37007802 Free PMC article.
-
A new species of buffalo leech in the genus Hirudinaria Whitman, 1886 (Arhynchobdellida, Hirudinidae) from Thailand.Zookeys. 2020 May 18;933:1-14. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.933.49314. eCollection 2020. Zookeys. 2020. PMID: 32508488 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Asian Buffalo Leech (Hirudinaria manillensis) Genome: Focus on Antithrombotic Genes and Their Corresponding Proteins.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 12;14(11):2068. doi: 10.3390/genes14112068. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003011 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of the cave leech Sinospelaeobdella cavatuses (Hirudinea: Haemadipsidae).Sci Data. 2024 Nov 13;11(1):1223. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-04007-3. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 39537640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai Y-T, Chen J-H. Leech fauna of Taiwan. Taiwan: National Taiwan University Press Taipei; 2010.
-
- Wagenaar DA. A classic model animal in the 21st century: recent lessons from the leech nervous system. J Exp Biol. 2015;218(21):3353–9. - PubMed
-
- Elliott JM, Kutschera U. Medicinal leeches: historical use, ecology, genetics and conservation. Freshwater Reviews. 2011;4(1):21–41.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

