The role of high knee range of motion at discharge on functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 40462011
- PMCID: PMC12135218
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-025-08802-w
The role of high knee range of motion at discharge on functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to investigate the impact of high knee range of motion at discharge on functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
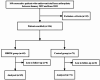
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of 136 patients with primary osteoarthritis who were treated between January 2022 and June 2023. Patients were classified according to the type of rehabilitation program: high range of motion (HROM) group or control group. In the HROM group, patients underwent high-intensity rehabilitation, especially without restricting the range of motion (ROM) following knee surgery. In the control group, patients received routine rehabilitation, with the affected knee achieving approximately 90 degrees of flexion at discharge. Patients' data related to postoperative knee ROM, Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) score, visual analogue scale (VAS) score, transfusion rate, wound complications, thrombus of lower limb, and usage of analgesic drugs were recorded to assess the influence of ROM at discharge on clinical outcomes.
Results: The HROM group had a higher knee ROM compared to the control group at discharge (P < 0.001). There were no significant differences between the HROM group and the control group in the basic demographic information, hospital stay and operation time (P > 0.05). HSS scores and knee ROM in the HROM group were significantly higher than those in the control group 1 and 2 months after surgery (P < 0.001). There were no significant differences in VAS at 1, 2 and 7 days after surgery between the two groups. The usage of analgesic drugs, wound complications, thrombus of lower limb, and transfusion rates were similar between the two groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusions: High knee ROM at discharge achieved through high-intensity rehabilitation is an effective and simple way to improve early knee mobility and function. The routine application of this protocol did not increase the incidence of wound complications.
Keywords: Discharge; Hospital for special surgery score; Range of motion; Total knee arthroplasty.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fuyang Hospital of Anhui Medical University. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (as revised in 2013). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Similar articles
-
Effect of Early Electroacupuncture Combined with Enhanced Recovery after Surgery (ERAS) on Pain Perception and Dysfunction in Patients after Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA).Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 9;2022:6560816. doi: 10.1155/2022/6560816. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9879057. doi: 10.1155/2023/9879057. PMID: 35586810 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Application of interrupted suture at exercise position in total knee arthroplasty].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 15;32(4):400-405. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201711067. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29806296 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[A prospective randomized controlled study of total knee arthroplasty via mini-subvastus and conventional approach].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 15;32(2):162-168. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201710075. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29806405 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Clinical application of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty in patient with bilateral knee osteoarthritis].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 15;34(12):1568-1573. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202005065. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33319537 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Effects of lower-limb active resistance exercise on mobility, physical function, knee strength and pain intensity in patients with total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Sep 12;25(1):730. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07845-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39267026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muraki S, et al. Association of radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis with health-related quality of life in a population-based cohort study in Japan: the ROAD study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(9):1227–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No. KJ2021ZD0034/the Major Natural Science Project of Universities in Anhui Province
- No. KJ2021ZD0034/the Major Natural Science Project of Universities in Anhui Province
- No. KJ2021ZD0034/the Major Natural Science Project of Universities in Anhui Province
- No. KJ2021ZD0034/the Major Natural Science Project of Universities in Anhui Province
- No. KJ2021ZD0034/the Major Natural Science Project of Universities in Anhui Province
- No. KJ2021ZD0034/the Major Natural Science Project of Universities in Anhui Province
- No.2022xkj071/the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University
- No.2022xkj071/the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University
- No.2022xkj071/the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University
- No.2022xkj071/the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University
- No.2022xkj071/the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University
- No.2022xkj071/the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical