Convergence of sepsis-associated encephalopathy pathogenesis onto microglia
- PMID: 40462103
- PMCID: PMC12131422
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06635-8
Convergence of sepsis-associated encephalopathy pathogenesis onto microglia
Abstract
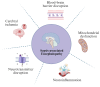
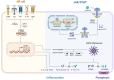
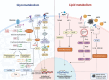
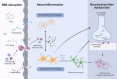
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is a neurological dysfunction induced by sepsis, with symptoms ranging from mild delirium to deep coma. About 70% of patients with severe systemic infection develop SAE and with more than half of surviving patients suffering from long-term cognitive deficits, which seriously damaged the quality of their daily life and brought a heavy burden to society. The pathogenesis of SAE is multifactorial, including activated inflammation, blood- brain barrier (BBB) disruption, cerebral blood flow impairment, and neurotransmitter disturbances. Microglia mediate multiple SAE pathologies. In this review, we summarized the most recent findings in the roles of microglia in every stage of SAE pathogenesis, focusing on the molecular pathways in microglia activation and downstream effects. We also demonstrated the novel therapeutic studies targeting microglia in SAE. Deep insight into the role of microglia in SAE is of great importance in exploring pathogenesis and developing effective remedies of SAE.
Keywords: Glycometabolism; Lipid metabolism; Microglia activation; Neuroinflammation; Neurological dysfunction; Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction.Inflammation. 2021 Dec;44(6):2143-2150. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01501-3. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 34291398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Central role of microglia in sepsis-associated encephalopathy: From mechanism to therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 26;13:929316. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.929316. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35958583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming of Microglia in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy: Insights from Neuroinflammation.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(9):1992-2005. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666221216162606. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36529923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microglia in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Sep;12(6):720-5. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660178. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24047519 Review.
-
[Research progress on the role of microglia in sepsis-associated encephalopathy].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Apr 25;76(2):289-300. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38658377 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Danielski LG, Giustina AD, Badawy M, Barichello T, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F, Petronilho F. Brain barrier breakdown as a cause and consequence of neuroinflammation in Sepsis. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55:1045–53. - PubMed
-
- Lelubre C, Vincent JL. Mechanisms and treatment of organ failure in sepsis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14:417–27. - PubMed
-
- Tauber SC, Djukic M, Gossner J, Eiffert H, Bruck W, Nau R. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and septic encephalitis: an update. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021;19:215–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82101443/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 82100551/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023-JC-JQ-60/Shaanxi Provincial Outstanding Young Scientist Fund Project
- 2022TD-47/Fund for Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Shaanxi Innovation Capability Support Plan
- 2023-CX-TD-67/Fund for Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Shaanxi Innovation Capability Support Plan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

